0% found this document useful (0 votes)
273 views64 pagesAir Distribution Systems Diffuser Selection
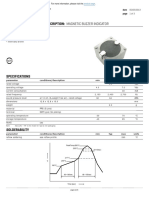
This document summarizes a lecture on air distribution system design. It discusses diffuser selection and classification into five groups based on location and air discharge characteristics. It also provides resources on fundamentals of air diffusion and diffuser location. The recap section defines characteristics room length and how to calculate it based on supply outlet location and throw. It discusses the importance of considering internal objects. The datasheets section explains how to read manufacturer datasheets and determine throw values. Finally, an example problem demonstrates using a manufacturer datasheet to select a suitable diffuser based on specified air flow and room layout.
Uploaded by
Sameh Aa2Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
273 views64 pagesAir Distribution Systems Diffuser Selection
This document summarizes a lecture on air distribution system design. It discusses diffuser selection and classification into five groups based on location and air discharge characteristics. It also provides resources on fundamentals of air diffusion and diffuser location. The recap section defines characteristics room length and how to calculate it based on supply outlet location and throw. It discusses the importance of considering internal objects. The datasheets section explains how to read manufacturer datasheets and determine throw values. Finally, an example problem demonstrates using a manufacturer datasheet to select a suitable diffuser based on specified air flow and room layout.
Uploaded by
Sameh Aa2Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 64