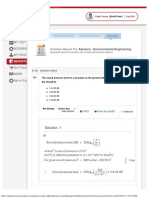
Numerical Python Indexing and Slicing
Numpy Cheat Sheet
NumPy provides a high-performance
Import convention multi-dimensional array object (ndarray), 1D Arrays 2D Arrays Advanced Indexing & Slicing
Indexing
>>> import numpy as np and tools for working with these arrays. Fancy Indexing
1 3 10 0 1 3 10 0 1 3 10 0 1 -2 0 1 -2 0 1 -2 0 >>> i = np.array([0,2])
>>> a[i]
3 4 2 3 4 2 3 4 2 [1,10]
Creating NumpyCreating
Arrays Numpy Arrays a[2] a[-3] a[0:2]
b[1,2] b[0] b[:,0]
>>> b[[0,2], [1,2]]
Creating From Lists 1D, 2D, 3D Numpy Arrays
Boolean Masking
Slicing >>> b[0:2] Slicing rows.
>>> np.array([3,4], dtype=float) >>> a = np.array([1, 3, 10, 0]) >>>m=np.array([True,False,False,True])
float array from list 1 3 10 0 1 5 5 5 >>> b[0:2,1:3] Slicing rows and >>> a[m]
columns. [1,0]
>>> b = np.array([[1, -2, 0], a[0:3:2] d[1:4]=5
[3, 4, 2]]) >>> b[:,0:2]=4 Modifying slices.
Creating Constant Numpy Arrays >>> c = np.array([[['A', 'B'],
['C', 'D'],
>>> np.zeros((3,4)) array of zeros
['E', 'F']],
>>> np.ones((2,3,4))
>>> e=np.full((3,4),7)
array of ones
constant array [['G', 'H'], Array Operations and Ufuncs Linear Algebra
['I', 'J'],
>>> np.matmul(b,e)
['K', 'L']]]) Operations on Numpy Arrays Relational Operations
Matrix
multiplication
Creating Sequential Arrays a(4,) b(2,3)
Operator Overloading >>> np.greater(a,l) a > l
>>> np.transpose(b) Transpose
axis 0
Arrays of evenly spaced values 1 -2 0 >>> np.greater_equal(a,l) a >= l
1 3 10 0 >>> np.add(a,l) is same as a + l
np.arange(10,25,5) step value axis 1 3 4 2 >>> np.less(a,l) a < l >>> np.linalg.det(f) Determinant
Vectorized Operations with NumPy
axis 0
axis 1 >>> np.less_equal(a,l) a >= l
l=np.linspace(0,3,4) # samples B D F >>> np.linalg.inv(f) Inverse
>>> np.equal(a,l) a >= l
A C E L Arithmetic Operations
axis 0
>>> np.not_equal(a,l) a >= l
2
np.empty((3,2)) empty array G I K Transpose
is
ax
>>> np.add(a,l) a + l
f=np.random.random((2,2)) random array c(2,3,2) array([1,4,12,3]) Bitwise Operations b b.T
>>> np.subtract(a,l) a - l
>>> np.bitwise_and(a,l) a & l
Other Array Construction Methods nD Array Properties >>> np.multiply(a,l) a * l
>>> np.bitwise_or(a,l) a | l
1 3
1 -2 0
>>> np.divide(a,l) a / l -2 4
>>> np.eye(2) 2 x 2 identity matrix >>> a.size Number of array elements >>> np.bitwise_xor(a,l) a ^ l
>>> np.floor_divide(a,l) a >/ l
3 4 2
>>> a.ndim Number of array dimensions >>> np.invert(a) ~a 0 2
>>> np.diag((1,3,5)) diagonal matrix
>>> a.shape Array dimensions >>> np.mod(a,l) a % l >>> np.left_shift(a,l) a >< l
>>> d = a.copy() Copy of array >>> a.dtype Data type of array elements >>> np.power(a,l) a >* l >>> np.right_shift(a,l) a >> l
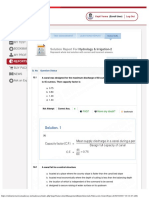
� Broadcasting & Masking Array Manipulations
Masking Changing shape of an array Splitting an array Tiling Arrays
Two arrays are said to be compatible in a dimension if
>>> np.reshape(c,(2,2,3)) >>> np.split(b, 2, Splits b into 2 >>> np.repeat(a,2) Repeats elements
1. they have the same size in that dimension, or C F
>>> mask = a > 3 B D F axis=0) equal arrays
2. one of the arrays has size 1 in that dimension B EI L
A C E L >>> np.hsplit(b,[2]) Splits at 2nd column
>>> a[mask] A H
D K Adding and Removing elements
>>> g = np.array([[1, -2, 0, 1], G I K G J
[3, 4, 2, 0]]) >>> np.vsplit(b,[1]) Splits at 1st row >>> np.delete(b,1,0) Deletes elements
>>> np.ravel(b)
>>> a + g 1 3 10 0 > 3 Contiguous flattened array >>> np.insert(b,1,
[4,4],axis=1)
Inserts elements
>>> b.flatten()
1 3 10 0
1 3 10 0 + 1 -2 0
3 4 2
1
0
False False True False
Flatten array to one dimension
>>> a[np.newaxis,:] Joining arrays
>>> np.append(a,l,
axis=0)
Appends elements
1 3 10 0 10 Increase dimension by one
2 1 10 1
>>> np.squeeze(a)
>>> np.concatenate( Joins sequence of Padding
4 7 12 0 (a,l), axis=0) arrays along axis
Removes single- dimensional entries >>> np.pad(b, (1,2), 'constant',
>>>np.hstack((a,l)) Stacks column-wise
constant_values=(-1,-2))
Changing the axes of an array >>>np.vstack((a,l)) Stacks row-wise Pads with a constant value.
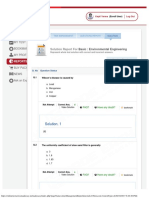
Useful Methods in Numpy More Numpy Methods >>> np.pad(b, (1, 1), 'edge')
>>> np.moveaxis(c, [0,1], [1, 2]) >>> np.stack([a, l], Joins along new axis.
>>> np.unique(a) Unique sorted elements Moves axes from old to new positions axis = 0) Pads with the edge values of the array.
Sum of all elements Maximum element
>>> np.where(a>5, If true a*2, else a*a >>> np.swapaxes(c, 1, 2)
>>> np.sum(a) >>> b.max() Interchanges axis-1 and axis-2
a*2, a*a)
>>> a.sum() >>>np.max(b,axis=0) hstack Edge padding
>>> np.add.reduce() >>> np.any(a) Any of the elements
evaluates to True ?
E F
B D F 1. 3. 10. 0. 0. 1. 2. 3.
C D L
K 1 1 -2 0 0
>>> np.argmax(a) Index of max element >>> np.all(a) All the elements evaluate A C E L
to True ? A BI J 1 1 -2 0 0
>>> np.sort(a) Sorted copy of array G I K G H vstack 3 3 4 2 2
2
>>> np.nan 1. 3. 10. 0.
2
NaN constant
is
is
ax
>>> a.sort() Sorts an array in-place
ax
axis 1 axis 1 3 3 4 2 2
>>> np.inf Positive Infinity 0. 1. 2. 3.
>>> np.argsort(a) Indices that sort array.