0% found this document useful (0 votes)
362 views6 pagesPT Science-5 Q2
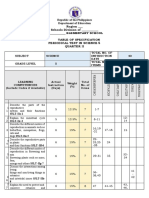
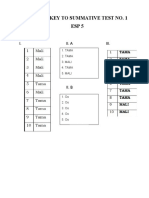
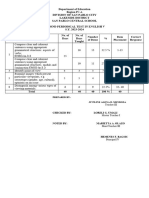
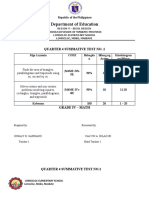
The document is a table of specifications for a science test on reproductive systems, modes of reproduction in different organisms, and interactions in estuaries and intertidal zones. It lists the competencies and breakdown of items by cognitive level (remember, understand, apply, analyze, evaluate, create). The test will have 50 total items covering: the parts of the reproductive system and their functions; the menstrual cycle; modes of reproduction in animals and plants; and interactions between living and non-living things in estuaries.
Uploaded by
Maria Antonia B. TalayCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
362 views6 pagesPT Science-5 Q2
The document is a table of specifications for a science test on reproductive systems, modes of reproduction in different organisms, and interactions in estuaries and intertidal zones. It lists the competencies and breakdown of items by cognitive level (remember, understand, apply, analyze, evaluate, create). The test will have 50 total items covering: the parts of the reproductive system and their functions; the menstrual cycle; modes of reproduction in animals and plants; and interactions between living and non-living things in estuaries.
Uploaded by
Maria Antonia B. TalayCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 6