0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1K views5 pagesMiddle-Level Management
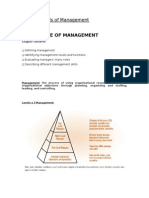
The document discusses middle-level management, defining it as positions that serve as a liaison between upper and lower level management to implement strategic plans and oversee operational functions. Examples of middle-level manager roles include department heads, regional managers, and factory managers. The key responsibilities of middle managers are developing tactical plans, overseeing staff, communicating between levels of management, and motivating subordinates.
Uploaded by
Diary Ali Abdalla HusseinCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1K views5 pagesMiddle-Level Management
The document discusses middle-level management, defining it as positions that serve as a liaison between upper and lower level management to implement strategic plans and oversee operational functions. Examples of middle-level manager roles include department heads, regional managers, and factory managers. The key responsibilities of middle managers are developing tactical plans, overseeing staff, communicating between levels of management, and motivating subordinates.
Uploaded by
Diary Ali Abdalla HusseinCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 5