0% found this document useful (0 votes)
92 views3 pagesDiffrent Types of Map
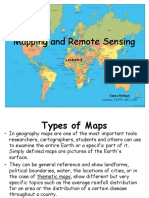
This document defines and describes different types of maps:
1. Topographic maps show both natural and human-made features using contour lines and other methods to indicate elevations and landforms.
2. Geologic maps indicate underground geological features and structures using symbols, colors, and orientation measurements.
3. Political maps delineate territorial boundaries and jurisdictions of areas, countries, or regions and identify major cities and landmasses.
Uploaded by
Ian GamitCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
92 views3 pagesDiffrent Types of Map
This document defines and describes different types of maps:
1. Topographic maps show both natural and human-made features using contour lines and other methods to indicate elevations and landforms.
2. Geologic maps indicate underground geological features and structures using symbols, colors, and orientation measurements.
3. Political maps delineate territorial boundaries and jurisdictions of areas, countries, or regions and identify major cities and landmasses.
Uploaded by
Ian GamitCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 3