0% found this document useful (0 votes)
57 views16 pagesNicardipine Drug Study Guide
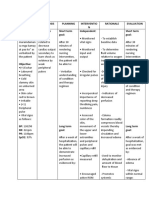
Nicardipine is a calcium channel blocker used to treat chronic stable angina, hypertension, and vasospastic angina. It works by inhibiting calcium ion entry into vascular smooth muscle and myocardial cells. Common side effects include blurred vision, dizziness, headache, and edema. Nurses monitor blood pressure and peripheral edema, ensure the right dose and route are given, and assess for signs of hypersensitivity.
Uploaded by
Hydie Mae AlcabedosCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
57 views16 pagesNicardipine Drug Study Guide
Nicardipine is a calcium channel blocker used to treat chronic stable angina, hypertension, and vasospastic angina. It works by inhibiting calcium ion entry into vascular smooth muscle and myocardial cells. Common side effects include blurred vision, dizziness, headache, and edema. Nurses monitor blood pressure and peripheral edema, ensure the right dose and route are given, and assess for signs of hypersensitivity.
Uploaded by
Hydie Mae AlcabedosCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 16