0% found this document useful (0 votes)
40 views9 pagesLecture 1-Introduction
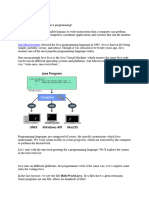
Java is a popular programming language created in 1995. It is used to create mobile apps, desktop apps, web apps, and more. Every Java program must contain a class with a main method that is the entry point for running the program. The main method uses System.out.println to print text to the screen. Programmers can add comments to documents to explain code.
Uploaded by
RozzellyCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
40 views9 pagesLecture 1-Introduction
Java is a popular programming language created in 1995. It is used to create mobile apps, desktop apps, web apps, and more. Every Java program must contain a class with a main method that is the entry point for running the program. The main method uses System.out.println to print text to the screen. Programmers can add comments to documents to explain code.
Uploaded by
RozzellyCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 9