0% found this document useful (0 votes)
112 views10 pagesRoad and Components
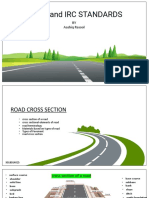
The document discusses different types of roads based on various factors such as materials, location and function, traffic volume, width, economics, traffic type, rigidity, and geography. Some key road types mentioned include earthen roads, gravel roads, murrum roads, kankar roads, water bound macadam roads, bituminous roads, and concrete roads. The document also discusses road components such as the carriageway, formation width, kerbs, road margins, medians, and camber. Location-based road types include national highways, state highways, district roads, and rural roads.
Uploaded by
Prakhar patidarCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
112 views10 pagesRoad and Components
The document discusses different types of roads based on various factors such as materials, location and function, traffic volume, width, economics, traffic type, rigidity, and geography. Some key road types mentioned include earthen roads, gravel roads, murrum roads, kankar roads, water bound macadam roads, bituminous roads, and concrete roads. The document also discusses road components such as the carriageway, formation width, kerbs, road margins, medians, and camber. Location-based road types include national highways, state highways, district roads, and rural roads.
Uploaded by
Prakhar patidarCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 10