0% found this document useful (0 votes)
48 views22 pagesSimple Programs
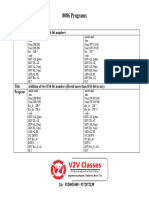
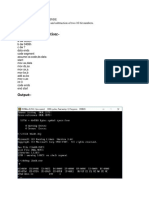
The document discusses 16 assembly language programs covering operations like incrementing, decrementing, complementing, adding, subtracting, multiplying, dividing, finding the sum and average of numbers, calculating factorials, and sorting arrays. The programs demonstrate how to perform these operations on 8-bit and 16-bit numbers using assembly language instructions.
Uploaded by
Jasmine KCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
48 views22 pagesSimple Programs
The document discusses 16 assembly language programs covering operations like incrementing, decrementing, complementing, adding, subtracting, multiplying, dividing, finding the sum and average of numbers, calculating factorials, and sorting arrays. The programs demonstrate how to perform these operations on 8-bit and 16-bit numbers using assembly language instructions.
Uploaded by
Jasmine KCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 22