MICRO ENVIRONMENT CHAPTER I
BUSINESS STUDIES
GRADE 10
TERM ONE
CHAPTER 1
MICRO ENVIRONMENT
2020
TABLE OF CONTENTS
TOPICS PAGES
Content details for teaching, learning and assessment 2
Meaning of micro environment: 2
Components/ features of the Micro Environment 2
Vision, Mission Statement, goal and objectives, 2-3
Organisational Culture 3
Organisational resources 4
Importance of the business organisational structure 4
Differences between management and leadership 5
Eight Business functions 5
Purpose of the eight business functions 5
Importance of business functions 5
General Management 6
Levels of management and the type of decisions taken by each 6-7
Management tasks 7-9
Types of organisational structures 9
This chapter consists of 9 pages
1
�MICRO ENVIRONMENT CHAPTER I
CONTENT DETAILS FOR TEACHING, LEARNING AND ASSESSMENT PURPOSES
Learners must be able to:
• Define/Explain the meaning of the micro environment
• Outline/Describe/Explain/Discuss the various components of the micro (internal business environment.
• Identify a vision, mission statement, goals and objectives from given scenarios.
• Formulate/Evaluate a vision, mission statement, goals and objectives of any business.
• Explain, Discuss the purpose of the organisational culture
• Outline/name/identify/Explain the organisational resources from given statements/scenarios.
• Describe the purpose/importance of a business organisational with specific reference to an
organogram.
• Explain the differences between leadership and management.
• Briefly explain the purpose of the eight business functions
• Outline/Describe/Explain/Explain the importance of the eight business functions.
BUSINESS ENVIRONMENTS (refer to the 2018 exam guideline page 6)
1 Micro environment/Internal environment
Meaning of micro environment/Internal environment
• It is the environment within which a business operates and consists of the business itself.
• It is the decision-making environment because management make decisions that help the business
achieve its goals.
• It can also be referred to as the immediate environment in which a business operates and includes all
the internal factors of the business.
2 Components/Features/ Elements of the Micro environment
The components of the micro environment include the following:
• Vision
• Mission
• Objectives
• Goals, strategy
• Organisational resources
• Leadership and management
• Business functions
• Organisational structure
• Organisational culture.
2.1 Explanation of the components/features/elements of the micro-environment
Vision
• Refers to a statement that explains what a business aims to achieve.
• Answer to the question: ‘where are going from here?’
• Sets out where the business needs to go to be successful
• The dream of the business and what it wants to achieve in future.
• Gives businesses a clear idea of what they want to achieve.
• The inspiring statement about what a business wants the future to look like.
• Explains what a business aims to achieve taking into consideration its purpose.
• Example ‘To provide job opportunities for the local community
2
�MICRO ENVIRONMENT CHAPTER I
Mission statement
• A statement that explains the reason for the business’s existence.
• Enables businesses to develop strategies to achieve their vision.
• The answer to the question such as: what do businesses do to make a profit?
• Explains what the business does to achieve its vision.
• Gives clear direction on how the business intends to achieve its vision.
• Describes the purpose and basic activities of the business.
• Example ‘To become a word-class communication company
Goals
• Can be defined as long term objectives of what the business wants to achieve.
• Goals breakdown the business’s objective into specific and measurable statement. Example Increase
profit margin by 50% in 2020.
• Goals give the business a sense of direction.
Objectives
• Short- term tasks/steps to reach goals.
• Contain a deadline for achievement.
• Explains how the goals of the business will be reached.
• Explains targets and strategies that will help the business fulfil its mission.
• The purpose of the business, for example, a business may have a primary objective of making a profit
and a secondary objective of social upliftment.
Strategy
• The strategy outlines how the business will achieve its vision in line with its mission statement and
objectives.
• It is a plan of action taken by top management to achieve their vision.
2.2 Purpose of the organisational culture
• It influences people’s actions and attitudes.
• The culture determines how things are done.
• It is the “personality” of the business.
• Shared understanding of how things are done in a business.
• Every business has a culture that is influenced by everyone who is part of it.
• It is based on three key issues: values, beliefs and purposes e.g. dress code/office décor/employee
behaviour etc.
• Influences the way people in the organisation interact with each other and with stakeholders.
2.2.1 Examples of the business culture
• Personality/ ethos of the business
• Norms, values and expectations.
• Business dress code
• Floor plan of the business.
• The working environment of the business.
• Respect for other employees’ values.
• The way managers are addressed
3
�MICRO ENVIRONMENT CHAPTER I
2.3 Organisational resources
• These are assets that the business uses to produce goods/services and to achieve its goals.
• The following four groups of resources are controlled by management:
Physical Financial Human Information &
resources/operating resources resources Technological
resources (People) resources
• Natural • Capital • Employees • Technology
resources • Own Capital • Contractors (the use of
• (raw material) • Cash computers)
• Machinery • Bank over • Research
• Vehicles drafts • Production
• Buildings • Short and technology
• Infrastructure medium term
• Assets from loans
nature such as • Money invested
water, minerals in the business
and wood to acquire
production
goods such as
land, building
and machinery
2.3.1 Explanation of types of Organisational resources
Human resource
• People with knowledge and skills such as employees/consultants/managers etc.
• The people needed to perform the work and keep the organisation functioning.
• People who contribute towards achieving the goals of the business.
Natural resources
• Assets from nature that are used to offer services and products, such as minerals, water and wood.
Physical resources
• Include raw materials/office furniture/equipment/machinery/plant necessary to operate the business
successfully.
Financial/Capital resources
• Money invested in the business to acquire production goods such as land, buildings and machinery.
• Can be in the form of cash/bank overdrafts/short and medium term loan
.
Technological resources
• Resources that include computers/voice mail/emails/production technology that gives the business an
advantage over its competitors.
Entrepreneurial resources
• The person responsible for combining the factors of production in such a way that the business will
make a profit.
2.4 Importance of business organisational structure
• It shows who report to whom and which department fall under which managers.
• The structure show the flow of instruction and feedback in the business.
• Every business must be organised into a structure that shows each person’s task, the level of authority
and responsibility.
• It is the hierarchy that shows the position of management, the departments and its employees.
4
�MICRO ENVIRONMENT CHAPTER I
2.5 Differences between leadership and management
MANAGEMENT LEADERSHIP
Managers ensures that tasks given to subordinates Leaders inspires other people
are completed
Task orientated People orientated
Uses Instructional approach Uses motivational approach
Uses Instructional approach Uses motivational approach
Managers hold a managerial position in the A leader does not hold a managerial position
business
Management is the process of achieving business Leadership is the process of inspiring and
goals influencing other to achieve business goals
Guides human behaviour Influences human behaviour
Communicates through management functions, Communicates by means of
e.g. line function. interaction/behaviour/vision/value s/ charisma.
A person becomes a manager because he/she is Leaders are born with natural/ instinctive leadership
appointed in the position skills
Manage by planning/organising/leading and Lead by example/trust/respect
controlling
2.6 Business functions
• General management
• Administration function
• Financial function
• Purchasing function
• Public function
• Human resources function
• Production function
• Marketing function
2.6.1 The purpose of the eight business functions
• The eight business functions work together to achieve the business goal.
• Each function carries out specific tasks which are closely linked in order to achieve the same goal.
• Roles and tasks may change depending on the size/type/stage of growth of the business.
• Business functions work together to ensure the survival and sustainability of the business.
2.6.2 Importance of business functions
• Sets the overall direction or strategy for the business.
• This function leads, organises and controls all the other functions.
• There are also decisions taken in each level.
• Management has three different levels, each with its own roles and responsibilities.
• Ensures that there is co-ordination among the seven different functions of the business.
5
�MICRO ENVIRONMENT CHAPTER I
BUSINESS OPERATIONS (Refer to the 2018 exam guidelines page 13-16)
1 GENERAL MANAGEMENT
Levels of management
• Levels of management mean the degree of power and authority that managers possess. The
following three levels of management are explained in detail:
Top management
• Reports to a board of directors/advisory board.
• Takes long term strategic decisions.
• Responsible for directing, controlling and managing risks.
• Determines the vision/mission/objectives/strategy of the business.
• Act of getting people together to accomplish certain goals.
• Oversees the activities of the other functions so that the business can achieve its objectives.
Middle management
• Responsible for specific departments within the business.
• Takes medium term tactical decisions.
• Responsible for achieving the goals and objectives set for the specific department.
• Concerned with implementing plans made by top level management.
• Implements the vision and plans of the top management.
• Responsible for working with managers in other departments and for acquiring resources needed
in their departments.
Lower management
• Responsible for a high level of productivity, technical assistance and motivating employees.
• Takes short term routine/tactical decisions.
• Carry out instructions given by middle management
• They are also called first management level as it is the first management level to which
subordinates can be promoted.
6
�MICRO ENVIRONMENT CHAPTER I
Levels of management and the type of decision taken by each.
Level of Type of decision Examples Roles
management
Top management Make long- term CEOs, -Plan the future of the business.
strategic decisions. directors, -Manage change in the business
(Policy), which will Owner of sole environment.
have long-term trader, -Plan the activities of the business.
outcomes/ partners in -Gives direction to the vision, mission,
Consequences. partnership goals and objectives.
Middle Make medium-term Departmental -Controls the people and processes in the
management tactical decisions. managers. e.g. business.
(Procedure) marketing -It is the link between top management
manager. and lower level management.
financial -Pass information from top management to
manager etc. lower management
-Focuses on how the business will carry
out the strategic decisions
-Acquire.
resources needed in their department
Lower level Make short-term Foreman, -Make routine activities.
operation decisions. supervisor, Plan the daily activities
team leaders. --Set individual objectives for workers
working under him/her.
-Offer feedback and suggestions to middle
management.
-Implement the objectives of the middle
management.
-They motivate and guide workers.
NOTE: You must be able to identify the levels of management from given statements and
scenarios
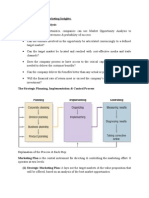
Management Tasks
• There are five basic management tasks which include the following:
o Planning
o Organising
o Leadership
o Controlling
o Risk management
• The above mentioned management tasks should be carried out at different levels of the business.
• These tasks are carried out to ensure that the vision, mission and goals of the business are met.
7
�MICRO ENVIRONMENT CHAPTER I
Planning
• The process of setting goals and developing strategies.
• It includes getting all the information you need for planning.
• Top management formulates strategic plans.
• Middle management formulates tactical plans.
• Lower management formulates operational plans
• Analysing the information and set long term goals.
• Considering different plans to achieve the goals.
• Choosing the best plan and decide on the action to be taken.
• Management looks ahead at the future to determine business objectives.
• Planning is done in all departments by all employees with the objectives of the company in mind.
• Process of setting goals and making plans to achieve these goals.
• Deciding on the backup plan to use if the chosen plan becomes impossible.
• Implementing the chosen plan.
• Follow up to make sure the plan is successful, adjust it or change to the backup plan.
Organising
• It is the mechanism used to execute the plan.
• Involves breaking a plan into action.
• The way in which people are grouped together.
• May also include training to ensure that the jobs are carried out successfully.
• Ensures successful execution of the plan by using relevant organisational structure.
• It looks at what needs to be done and organizing resources need to achieve goals and objectives.
• Organising the jobs within specific functions or departments.
• People must understand what is expected from them in terms of tasks/ authority /
responsibility etc.
• Employees must know the organisational procedures for instructions and feedback and which
resources they can use.
Leading/Directing/Activating /
• The process of leading is to guide, motivate and inspire others to achieve goals.
• Refers to inspiring employees to carry out their task to the best of their abilities.
• Establishing a productive working climate.
• Motivating employees to achieve the goals set.
• Guiding employees in the right direction so that the business can achieve its goals.
• Activating workers to use their skills and resources to their best ability.
• Providing employees with directions on how things should be done.
• Respecting and treating employees so that they work willingly to achieve the business goals.
• Leaders set up proper communication channels so that the workers are always informed and
there is clear transfer of information.
Controlling
• Ensures that the business achieve its goals.
• Ensures that standards are met
• Ensures activities are carried out as planned.
• Enables the business to take corrective measures if the objectives are not achieved.
• Risk can be identified during control.
• Involves comparing actual results with goals set by management
• Corrective measures must be taken if there is a difference between actual results and the goals
the business set out to achieve.
• Continuous control ensures that the business runs smoothly. .
8
�MICRO ENVIRONMENT CHAPTER I
Risk Management
• Identifies possible risk by finding risk-bearing activities (i.e. activities which could go wrong) within the
organisation.
• Assists businesses to analyse each possible risk to assess how likely it is that the risk will happen.
• Evaluates the potential impact of risk in terms of financial liability.
• Controls/Monitors the risk by studying reports and trends in the environment so that measures can be
taken to prevent it from happening.
• Handles the risk by determining what actions to take should the event happen
• This can be done using available resources, contingency plans and communication with stakeholders.
2 ORGANISATIONAL STRUCTURES
2.1 Factors that influence the organisation structure
• The size of the company
• Technology
• Resources
• Strategic goals of the company.
2.2 Types of organisational structures
Functional organisational structure
• Employees get instructions from more than one manager
• The plan to be carried out determines who will be giving instructions
• This structure confuses employees as they report to more than one manager.
Project Organisational structure
• This is structured around project teams
• It is a temporary structure because employees are drawn from different departments
• Employees are then grouped together to form a project team which will carry out a particular project.
Matrix Organisational structure
• This structure is structured around projects but employees stay in their departments.
• A project must be completed up to a certain point
• The project is then passed on to the next team, which will carry out the next phase of the project.
Line organisational structure
• Employees report to only one person
• Only the Director can give instructions to employees
• This structure eliminates confusion among employees as they report to one person only
Line and staff organisational structure
• Experts act as advisors to top and middle management.
• Advisors don’t form part of the business, they merely give advice
• Advisors don’t have authority over the employees which means they can’t give any instruction to
employees.