0% found this document useful (0 votes)
71 views4 pagesDual Nature of Radiations and Matter
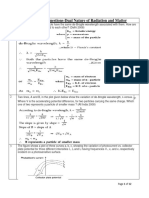
The document contains 8 questions about the dual nature of matter and radiation. The questions cover topics like the de Broglie wavelength, kinetic energy, and momentum of electrons and protons. They also discuss photoelectric effect, work function, and how factors like radiation frequency and intensity affect photoelectric emission.
Uploaded by
seakanugaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
71 views4 pagesDual Nature of Radiations and Matter
The document contains 8 questions about the dual nature of matter and radiation. The questions cover topics like the de Broglie wavelength, kinetic energy, and momentum of electrons and protons. They also discuss photoelectric effect, work function, and how factors like radiation frequency and intensity affect photoelectric emission.
Uploaded by
seakanugaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 4