0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views8 pagesFinancial Accounting and Analysis
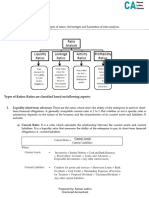
The document discusses various accounting concepts and ratios used to analyze the financial performance of companies. It provides definitions and calculations of key ratios like current ratio and quick ratio. Current ratio is the ratio of current assets to current liabilities and measures a company's ability to pay short-term debts. Quick ratio further refines this by excluding inventory from current assets, since it is not as readily convertible to cash. The document also provides examples of revenue, expenses, and other income classification in financial statements.
Uploaded by
divyakashyapbharat1Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views8 pagesFinancial Accounting and Analysis
The document discusses various accounting concepts and ratios used to analyze the financial performance of companies. It provides definitions and calculations of key ratios like current ratio and quick ratio. Current ratio is the ratio of current assets to current liabilities and measures a company's ability to pay short-term debts. Quick ratio further refines this by excluding inventory from current assets, since it is not as readily convertible to cash. The document also provides examples of revenue, expenses, and other income classification in financial statements.
Uploaded by
divyakashyapbharat1Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 8