0% found this document useful (0 votes)
38 views29 pagesFitness Centre Project Certificate
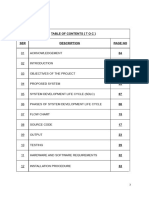
This document contains information about a fitness center project being developed for PM Shri School in Odisha, India for the 2023-2024 session. It includes a certificate confirming the completion of the project work, an acknowledgement section thanking those involved, and a table of contents outlining the various sections of the project report. The report will cover the introduction, objectives, proposed system, system development life cycle phases, flow chart, source code, output, testing, hardware and software requirements, installation procedure, and bibliography.
Uploaded by
saisantosh63721Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
38 views29 pagesFitness Centre Project Certificate
This document contains information about a fitness center project being developed for PM Shri School in Odisha, India for the 2023-2024 session. It includes a certificate confirming the completion of the project work, an acknowledgement section thanking those involved, and a table of contents outlining the various sections of the project report. The report will cover the introduction, objectives, proposed system, system development life cycle phases, flow chart, source code, output, testing, hardware and software requirements, installation procedure, and bibliography.
Uploaded by
saisantosh63721Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 29