0% found this document useful (0 votes)
47 views23 pagesLoops and Arrays
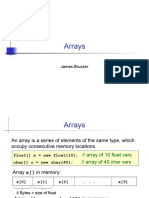
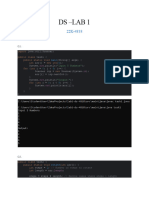
The document discusses loops and arrays in Java. It defines loops as control structures that repeatedly execute parts of a program if a condition is true. There are four main types of loops: for, for-each, while, and do-while. Arrays allow storing multiple values in a single variable rather than separate variables. Arrays can be single-dimensional or multi-dimensional. Elements in an array are accessed using indexes and the length of an array can be determined. Several problems demonstrate using loops and accessing, changing, and determining lengths of arrays.
Uploaded by
callmeazu25Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
47 views23 pagesLoops and Arrays
The document discusses loops and arrays in Java. It defines loops as control structures that repeatedly execute parts of a program if a condition is true. There are four main types of loops: for, for-each, while, and do-while. Arrays allow storing multiple values in a single variable rather than separate variables. Arrays can be single-dimensional or multi-dimensional. Elements in an array are accessed using indexes and the length of an array can be determined. Several problems demonstrate using loops and accessing, changing, and determining lengths of arrays.
Uploaded by
callmeazu25Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 23