0% found this document useful (0 votes)
102 views2 pagesRib Comp Questions
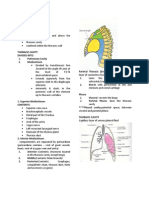
This document contains questions and answers about ribcage anatomy and radiographic examination of the ribs. It asks about the purpose of the ribcage, classifications of ribs, rib anatomy, vertebral level correlations, ideal imaging techniques for upper and lower ribs including patient positioning and visible anatomy. It also discusses common rib pathologies and additional imaging that may be needed in cases of rib fractures.
Uploaded by
amysjohnson17Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
102 views2 pagesRib Comp Questions
This document contains questions and answers about ribcage anatomy and radiographic examination of the ribs. It asks about the purpose of the ribcage, classifications of ribs, rib anatomy, vertebral level correlations, ideal imaging techniques for upper and lower ribs including patient positioning and visible anatomy. It also discusses common rib pathologies and additional imaging that may be needed in cases of rib fractures.
Uploaded by
amysjohnson17Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 2