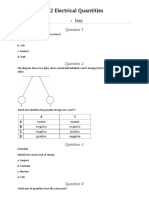
A student set up the electrical circuit shown in the figure below.
(a) The ammeter displays a reading of 0.10 A.
Calculate the potential difference across the 45 Ω resistor.
.............................................................................................................................
.............................................................................................................................
Potential difference = ............................................. V
(2)
(b) Calculate the resistance of the resistor labelled R.
.............................................................................................................................
.............................................................................................................................
.............................................................................................................................
Resistance = ............................................. Ω
(3)
(c) State what happens to the total resistance of the circuit and the current through the circuit
when switch S is closed.
.............................................................................................................................
.............................................................................................................................
.............................................................................................................................
.............................................................................................................................
(2)
(Total 7 marks)
Page 2 of 17
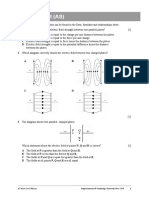
� (a) Figure 1 shows the oscilloscope trace an alternating current (a.c.) electricity supply
2 produces.
Figure 1
One vertical division on the oscilloscope screen represents 5 volts.
Calculate the peak potential difference of the electricity supply.
.............................................................................................................................
Peak potential difference = ................................................. V
(1)
(b) Use the correct answer from the box to complete the sentence.
40 50 60
In the UK, the frequency of the a.c. mains electricity supply is ............ hertz.
(1)
(c) Figure 2 shows how two lamps may be connected in series or in parallel to the 230 volt
mains electricity supply.
Figure 2
Page 3 of 17
� (i) Calculate the potential difference across each lamp when the lamps are connected in
series.
The lamps are identical.
...................................................................................................................
Potential difference when in series = ..................... V
(1)
(ii) What is the potential difference across each lamp when the lamps are connected in
parallel?
Tick (✔) one box.
115 V 230 V 460 V
(1)
(iii) Give one advantage of connecting the lamps in parallel instead of in series.
...................................................................................................................
...................................................................................................................
(1)
(d) Figure 3 shows the light fitting used to connect a filament light bulb to the mains electricity
supply.
Figure 3
The light fitting does not have an earth wire connected.
Explain why the light fitting is safe to use.
.............................................................................................................................
.............................................................................................................................
.............................................................................................................................
.............................................................................................................................
(2)
Page 4 of 17
� (e) A fuse can be used to protect an electrical circuit.
Name a different device that can also be used to protect an electrical circuit.
.............................................................................................................................
(1)
(Total 8 marks)
(a) Figure 1 shows the inside of a battery pack designed to hold three identical 1.5 V cells.
3
Figure 1
Which one of the arrangements shown in Figure 2 would give a 4.5 V output across the
battery pack terminals T?
Figure 2
(1)
(b) Figure 3 shows a variable resistor and a fixed value resistor connected in series in a
circuit.
Figure 3
Complete Figure 3 to show how an ammeter would be connected to measure the current
through the circuit.
Use the correct circuit symbol for an ammeter.
(1)
Page 5 of 17
�(c) The variable resistor can be adjusted to have any value from 200 ohms to 600 ohms.
Figure 4 shows how the reading on voltmeter V1 and the reading on voltmeter V2 change
as the resistance of the variable resistor changes.
Figure 4
(i) How could the potential difference of the battery be calculated from Figure 4?
Tick (✔) one box.
9 + 3 = 12 V
9–3=6V
9÷3=3V
Give the reason for your answer.
...................................................................................................................
...................................................................................................................
(2)
Page 6 of 17
� (ii) Use Figure 4 to determine the resistance of the fixed resistor, R.
Resistance of R = ..................... Ω
Give the reason for your answer.
...................................................................................................................
...................................................................................................................
(2)
(iii) Calculate the current through the circuit when the resistance of the variable resistor
equals 200 Ω.
...................................................................................................................
...................................................................................................................
...................................................................................................................
Current = ..................... A
(3)
(Total 9 marks)
The current in a circuit depends on the potential difference provided by the cells and the total
4 resistance of the circuit.
(a) Figure 1 shows the graph of current against potential difference for a component.
What is the name of the component?
Draw a ring around the correct answer.
diode filament bulb thermistor
(1)
Page 7 of 17
�(b) Figure 2 shows a circuit containing a 6 V battery.
Two resistors, X and Y, are connected in parallel.
The current in some parts of the circuit is shown.
(i) What is the potential difference across X?
Potential difference across X = ............................. V
(1)
(ii) Calculate the resistance of X.
...............................................................................................................
...............................................................................................................
Resistance of X = ............................. Ω
(2)
Page 8 of 17
�(iii) What is the current in Y?
Current in Y = ............................. A
(1)
(iv) Calculate the resistance of Y.
...............................................................................................................
Resistance of Y = ............................. Ω
(1)
(v) When the temperature of resistor X increases, its resistance increases.
What would happen to the:
• potential difference across X
• current in X
• total current in the circuit?
Tick ( ) three boxes.
Decrease Stay the same Increase
Potential difference across X
Current in X
Total current in the circuit
(3)
(Total 9 marks)
Page 9 of 17
� (a) Draw one line from each circuit symbol to its correct name.
5
Circuit symbol Name
Diode
Light-
dependent
resistor
(LDR)
Lamp
Light-
emitting
diode (LED)
(3)
Page 10 of 17
�(b) Figure 1 shows three circuits.
The resistors in the circuits are identical.
Each of the cells has a potential difference of 1.5 volts.
Figure 1
Circuit 1 Circuit 2 Circuit 3
(i) Use the correct answer from the box to complete the sentence.
half twice the same as
The resistance of circuit 1 is ................................................ the resistance of circuit
3.
(1)
(ii) Calculate the reading on voltmeter V2.
...............................................................................................................
Voltmeter reading V2 = .............................. V
(1)
(iii) Which voltmeter, V1, V2 or V3, will give the lowest reading?
Draw a ring around the correct answer.
V1 V2 V3
(1)
Page 11 of 17
�(c) A student wanted to find out how the number of resistors affects the current in a series
circuit.
Figure 2 shows the circuit used by the student.
Figure 2
The student started with one resistor and then added more identical resistors to the circuit.
Each time a resistor was added, the student closed the switch and took the ammeter
reading.
The student used a total of 4 resistors.
Figure 3 shows three of the results obtained by the student.
Figure 3
Number of resistors in series
(i) To get valid results, the student kept one variable the same throughout the
experiment.
Which variable did the student keep the same?
...............................................................................................................
(1)
Page 12 of 17
� (ii) The bar chart in Figure 3 is not complete. The result using 4 resistors is not shown.
Complete the bar chart to show the current in the circuit when 4 resistors were used.
(2)
(iii) What conclusion should the student make from the bar chart?
...............................................................................................................
...............................................................................................................
(1)
(Total 10 marks)
The picture shows an electric cooker hob. The simplified circuit diagram shows how the four
6 heating elements connect to the mains electricity supply. The heating elements are identical.
When all four heating elements are switched on at full power the hob draws a current of 26 A
from the 230 V mains electricity supply.
(a) Calculate the resistance of one heating element when the hob is switched on at full power.
Give your answer to 2 significant figures.
........................................................................................................................
........................................................................................................................
........................................................................................................................
Resistance = .............................. Ω
(3)
Page 13 of 17
�(b) The table gives the maximum current that can safely pass through copper wires of different
cross-sectional area.
Cross-sectional Maximum safe
area in mm2 current in amps
1.0 11.5
2.5 20.0
4.0 27.0
6.0 34.0
The power sockets in a home are wired to the mains electricity supply using cables
containing 2.5 mm2 copper wires. Most electrical appliances are connected to the mains
electricity supply by plugging them into a standard power socket.
It would not be safe to connect the electric cooker hob to the mains electricity supply by
plugging it into a standard power socket.
Why?
........................................................................................................................
........................................................................................................................
........................................................................................................................
........................................................................................................................
(2)
(c) Mains electricity is an alternating current supply. Batteries supply a direct current.
What is the difference between an alternating current and a direct current?
........................................................................................................................
........................................................................................................................
........................................................................................................................
........................................................................................................................
(2)
(Total 7 marks)
Page 14 of 17
� (a) The diagram shows the circuit that a student used to investigate how the current through a
7 resistor depends on the potential difference across the resistor.
(i) Each cell provides a potential difference of 1.5 volts.
What is the total potential difference provided by the four cells in the circuit?
...............................................................................................................
Total potential difference = .................................................. volts
(1)
(ii) The student uses the component labelled X to change the potential difference across
the resistor.
What is component X?
Draw a ring around your answer.
light-dependent resistor thermistor variable resistor
(1)
(iii) Name a component connected in parallel with the resistor.
...............................................................................................................
(1)
Page 15 of 17
�(b) The results obtained by the student have been plotted on a graph.
(i) One of the results is anomalous.
Draw a ring around the anomalous result.
(1)
(ii) Which one of the following is the most likely cause of the anomalous result?
Put a tick ( ) in the box next to your answer.
The student misread the ammeter.
The resistance of the resistor changed.
The voltmeter had a zero error.
(1)
(iii) What was the interval between the potential difference values obtained by the
student?
...............................................................................................................
...............................................................................................................
(1)
Page 16 of 17
�(c) Describe the relationship between the potential difference across the resistor and the
current through the resistor.
........................................................................................................................
........................................................................................................................
(1)
(Total 7 marks)
Page 17 of 17