TKM College of Engineering Kollam -5
III Semester Civil Engineering
Tutorial 1
CE309 Fluid Mechanics-I
1. Find the weight of 10 litres of oil of specific gravity 0.5 [Ans 49.05 N]
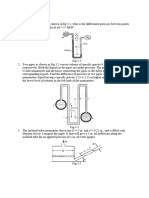
2. A gauge indicated a pressure of 40 kPa, barometric reading is 740 mm of mercury.
Compute pressure in terms of
a. Meters of water (gauge) [Ans 4.077 m]
b. Meters of mercury (gauge) [Ans 0.29 m]
c. N/m2 (absolute) [Ans 138.73 kPa]
d. Meters of water (absolute) [Ans 14.14 m]
e. Meters of mercury (absolute) [Ans 1.04 m]
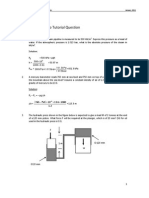
3. A U-tube manometer is used to measure the pressure of water in a pipeline which is in
excess of atmospheric. The left limb is connected to the pipeline and right limb is open to
atmosphere. The free surface of mercury in the right limb is in level with the centre line of
the pipe and the level difference of mercury in the limbs of the manometer is 20 cm.
Compute the water pressure in the pipeline. If the pressure of water is increased by 50 %,
compute the manometric reading.[ Ans 24.72 kPa; h=0.048 m; 0.296 m]
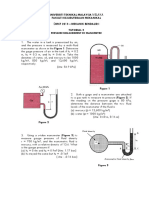
4. A differential manometer is used to measure the difference of pressure of oil of specific
gravity 0.8 contained in two pipes at the same level. If the deflection of manometric liquid,
which is mercury is to be 100 mm, determine the difference of pressure of oil in the two
pipes. [Ans 12.55 kPa]
5. To measure the pressure difference of water flowing through two pipes A & B, a U-tube is
used to connect two pipes. Difference of mercury between the two limbs of U-tube is 25
cm with the level in the left limb being at upper position. The centerline of pipe B is 2 m
below the centerline and to the right side of A, compute the difference of pressure in the
two pipes. [ Ans 50.5 kPa]
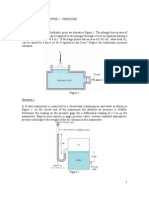
6. Two pressure points in a water pipe are connected to a manometer which has the form of an
inverted U-tube. The space above the water in the two limbs of the manometer is filled with
toluene of specific gravity 0.875. If the difference of water columns in the two limbs is 120
mm, compute the corresponding difference of pressure between the points in bar. [15*10-4]
7. A tank with vertical sides is square in plan. The sides are 1.5 m long. It contains water to a
depth of 1 m and oil of sp. gravity 0.9 to a depth of 1.2 m. Find (i) total pressure on each
side of the tank; (ii) position of centre of pressure above the base of the tank
[ (0.535+15.892+7.3573) kN at 0.724 m from the base]
8.. A trapezoidal masonry dam having water on its vertical side is 18 m high. The widths of
the dam at the base and top are 8 m and 4 m. Water is up to a height of 15 m. If the weight
of masonry is 20 kN/m3, find the resultant force per m length (ii) point where it cuts the
base. [ P=1103.6 kN per m length ; W=2118.96 N]