0% found this document useful (0 votes)
841 views7 pagesInstruction Set in 8051 Microcontroller
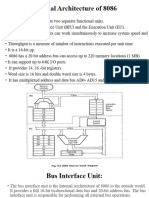
The document summarizes the instruction set of the 8051 microcontroller. It describes 5 categories of instructions: arithmetic, branch, data transfer, logical, and bit-oriented. The arithmetic instructions perform operations like addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division. The branch instructions include unconditional jumps, conditional jumps, and subroutine calls. The data transfer instructions move data between registers and memory.
Uploaded by
Ajnamol N RCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
841 views7 pagesInstruction Set in 8051 Microcontroller
The document summarizes the instruction set of the 8051 microcontroller. It describes 5 categories of instructions: arithmetic, branch, data transfer, logical, and bit-oriented. The arithmetic instructions perform operations like addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division. The branch instructions include unconditional jumps, conditional jumps, and subroutine calls. The data transfer instructions move data between registers and memory.
Uploaded by
Ajnamol N RCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 7