0% found this document useful (0 votes)
84 views18 pagesCryptography Lab Manual
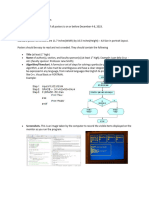
The document provides code implementations for various cryptographic techniques including transposition ciphers (Rail Fence and Columnar Transposition), substitution ciphers (Caesar and Vigenère ciphers), and asymmetric key algorithms (Diffie-Hellman key exchange and RSA). Menu-based applications are created to demonstrate encrypting/decrypting texts using the different techniques. Functions for encryption and decryption are defined for each technique. Practicals 1-4 provide code for the transposition/substitution ciphers and Diffie-Hellman and RSA algorithms. Practical 5 outlines a function for solving the 0/1 Knapsack problem using dynamic programming.
Uploaded by
Dhruv SanganiCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
84 views18 pagesCryptography Lab Manual
The document provides code implementations for various cryptographic techniques including transposition ciphers (Rail Fence and Columnar Transposition), substitution ciphers (Caesar and Vigenère ciphers), and asymmetric key algorithms (Diffie-Hellman key exchange and RSA). Menu-based applications are created to demonstrate encrypting/decrypting texts using the different techniques. Functions for encryption and decryption are defined for each technique. Practicals 1-4 provide code for the transposition/substitution ciphers and Diffie-Hellman and RSA algorithms. Practical 5 outlines a function for solving the 0/1 Knapsack problem using dynamic programming.
Uploaded by
Dhruv SanganiCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 18