1
Welcome to E-commerce (EHAD3000D)
Mohammad Ejaz
�E-commerce business strategies
3
�Objectives of teaching
• Identify and explain key elements of business
model
• Describe major business models in e-commerce
• Explain central concepts and business strategies
that are applicable to e-commerce
4
�What is business model?
• A set of planned activities designed to result in a
profit
• A collaborative process of creating, capturing, and
delivering value to stakeholders
• Multiple stakeholders contribute with valuable and
unique resources
5
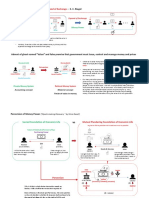
�The eight key elements of a business model
6
�Value proposition
• Why should the customer buy from you?
• Solving problems, providing comfort, and fulfilling
needs of customers and users
• Reduction of cost, enhancement of satisfaction, fast
product and service distribution, secure
transaction, and reduction of search time
7
�Revenue model
• How will you earn money?
• Mode of earning revenue, generating profits, and
providing returns on invested capital
• Advertising revenue model
• Transaction fee revenue model
• Sales revenue model
8
�Competitive environment
• What market place do you intend to serve, and what is its
size?
• Firms rely on environment for resources and return on
investment
• Presence of competitors and their market share
• Potential for emergence of new competitors
• Suppliers and their role in market
9
�Competitive advantage
• Who else operates in intended marketplace?
• Production and distribution of products and
services at lower costs than other companies
• Occupy market share and increase customer
satisfaction
• Build collaborative relationships with stakeholders
10
�Market strategy
• How do you plan to promote your products or
services to attract your customers and users?
• Communicate value creation potential
• Promote products and service through marketing
channels in order to inform, motivate, and remind
11
�Organizational development
• What type of organizational structure is important?
• How the company will organize the work?
• Creation of functional departments (production,
finance, and marketing)
12
�Management team
• What type of experiences, skills, and background
are necessary for management?
• Human capital is a source of competitive and
strategic advantage
• Identifying people who could achieve critical tasks
13
�Major business-to-consumer (B2C)
business models
• Value proposition: convenience, global accessibility,
time-saving, low-priced
• Revenue models: selling of products and services,
subscriptions, and advertising
14
�E-tailer
• Offers products and services to consumers through online
store
• Consumers can buy whenever and wherever they want, as
e-tailer is reachable 24/7
• Amazon.com and oda.com
• Disadvantages: consumers cannot see products and need to
wait for delivery
15
�Community providers
• Create a meeting place for transaction, sharing of videos,
and exchanging of ideas for like-minded people
• Reddit.com, facebook.com, twitter.com
• The share price of GameStop have increase from 18 to 350
dollars because of users of Reddit
16
�Content providers
•Distribute information, videos, music, and
photos
•Dinepenger.no, vg.no, youtube.com, and
financialtimes.com
•Revenue models: subscriptions, and
advertising
17
�Portal
• Combination of search tools and services
• Provide access to news, emails, maps, calendars,
shopping, and music
• Google, Bing, Yahoo, and Baidu
18
�Transaction broker
• Facilities online transactions for customers
• Value proposition: security, time saving, and cost
saving
• Revenue model: earns money when a transaction
takes place
• Financial and travel services
• Norndnet.no, robinhood.com, hotels.com
19
�Market creator
• Creates a marketplace for buyers and sellers
• Revenue models: digital display advertising,
transaction fees
• Finn.no, penger.no
20
�Service provider
• Many developed countries are service dominated
economies
• Service sector have been growing faster than
manufacturing sector
• Penger.no, momendo.no
21
�How e-commerce changes business, strategy,
structure, and process
• Industry structure: nature of actors
and their bargaining power
• Characterises by five forces:
1. Rivalry among existing competitors
2. Barriers to entry
3. Threat of substitute products
4. Bargaining power of suppliers
5. Bargaining power of buyers
22
�Industry value chain
• Set of activities performed in an industry that transforms raw input into
final products and services
23
�Firm value chain
•E-commerce provides opportunities to
improve production and distribution
•Building of global networks with suppliers
•Connecting with diverse suppliers in order to
fulfil needs of consumers
24
�Firm value webs
• Suppliers and distributors of a firm are connected with thier business
partners
25
�Business strategy
• Plans for achieving superior returns on investment compared to
competitors
26
�Four strategies
• Differentiation: process of creating unique and different
products and services
• Cost: process of utilising unique resources to reduce costs
• Scope: acquiring of capabilities to compete in all markets
• Focus: operating within a narrow market or segment
27