0% found this document useful (0 votes)
45 views27 pages06 Research Process
The document discusses key aspects of research design such as:
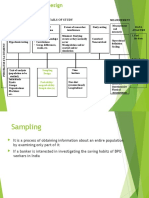
1) Research design provides the overall plan and guidelines for conducting research from start to finish, helping ensure validity and efficiency.
2) It addresses what data is needed, how it will be collected and analyzed, required resources, and desired accuracy levels.
3) Research design involves determining sampling strategies, observational methods, statistical tests, and operational procedures.
4) Common types of research design include correlational, experimental, qualitative, and meta-analysis. Sampling methods can be random or non-random.
Uploaded by
DAVALDARIYA WALIKARCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
45 views27 pages06 Research Process
The document discusses key aspects of research design such as:
1) Research design provides the overall plan and guidelines for conducting research from start to finish, helping ensure validity and efficiency.
2) It addresses what data is needed, how it will be collected and analyzed, required resources, and desired accuracy levels.
3) Research design involves determining sampling strategies, observational methods, statistical tests, and operational procedures.
4) Common types of research design include correlational, experimental, qualitative, and meta-analysis. Sampling methods can be random or non-random.
Uploaded by
DAVALDARIYA WALIKARCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 27