0% found this document useful (0 votes)
68 views11 pagesTelecom Architecture Evolution With Technology
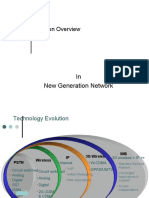
The document discusses the evolution of telecom network architectures from 2G to 4G. It covers the architectures of GSM, UMTS, IMS, and LTE networks and highlights the key changes and enhancements in each generation including transitioning to an all-IP architecture and separation of control and user planes.
Uploaded by
rogehkarout5Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
68 views11 pagesTelecom Architecture Evolution With Technology
The document discusses the evolution of telecom network architectures from 2G to 4G. It covers the architectures of GSM, UMTS, IMS, and LTE networks and highlights the key changes and enhancements in each generation including transitioning to an all-IP architecture and separation of control and user planes.
Uploaded by
rogehkarout5Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 11