0% found this document useful (0 votes)
76 views6 pagesIntroduction To Cellular Mobile System
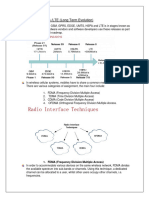
This document discusses the history and evolution of cellular mobile systems from 1G to 5G networks. It provides details on each generation including the technologies used, features, and limitations. The key points are: 1) Wireless communication enables transmission without wires, 2) Cellular networks have advanced from analog 1G to digital 2G/3G/4G networks with higher speeds and capacities, 3) 5G is the next generation still being developed to provide speeds over 1 Gbps and connect many devices simultaneously.
Uploaded by
khushijahnvi20Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
76 views6 pagesIntroduction To Cellular Mobile System
This document discusses the history and evolution of cellular mobile systems from 1G to 5G networks. It provides details on each generation including the technologies used, features, and limitations. The key points are: 1) Wireless communication enables transmission without wires, 2) Cellular networks have advanced from analog 1G to digital 2G/3G/4G networks with higher speeds and capacities, 3) 5G is the next generation still being developed to provide speeds over 1 Gbps and connect many devices simultaneously.
Uploaded by
khushijahnvi20Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 6