0% found this document useful (0 votes)
110 views11 pagesOral Comm DLL Week 5
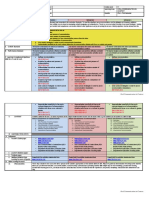
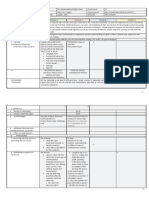
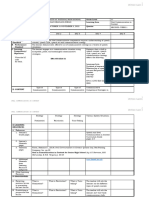
The document outlines the objectives, content, learning resources, and procedures for a lesson on oral communication, which includes identifying the speaker's purpose, watching sample activities, and comprehending different types of oral texts. The lesson will cover purposes like informing, persuading, and entertaining, and present examples such as interviews, debates, storytelling, and speeches. Students will write a 250-word essay evaluating speakers they observed.
Uploaded by
jenelfa.lopezCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
110 views11 pagesOral Comm DLL Week 5
The document outlines the objectives, content, learning resources, and procedures for a lesson on oral communication, which includes identifying the speaker's purpose, watching sample activities, and comprehending different types of oral texts. The lesson will cover purposes like informing, persuading, and entertaining, and present examples such as interviews, debates, storytelling, and speeches. Students will write a 250-word essay evaluating speakers they observed.
Uploaded by
jenelfa.lopezCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 11