0% found this document useful (0 votes)
29 views28 pagesHuman Reproductive System
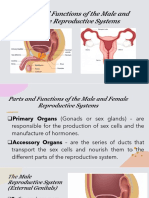
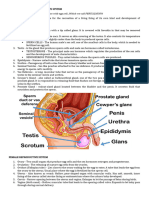
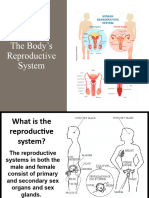
The human reproductive system consists of internal and external organs that work together to produce offspring. The male reproductive system produces, maintains, and transports sperm and semen. The female reproductive system produces eggs, receives sperm, and nurtures the development of offspring. Key parts include testes, ovaries, uterus, and other organs that play roles in hormone production, fertilization, and pregnancy.
Uploaded by
Xyrhuz SedilloCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
29 views28 pagesHuman Reproductive System
The human reproductive system consists of internal and external organs that work together to produce offspring. The male reproductive system produces, maintains, and transports sperm and semen. The female reproductive system produces eggs, receives sperm, and nurtures the development of offspring. Key parts include testes, ovaries, uterus, and other organs that play roles in hormone production, fertilization, and pregnancy.
Uploaded by
Xyrhuz SedilloCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 28