0% found this document useful (0 votes)
140 views6 pagesExcel Automation - Cheatsheet
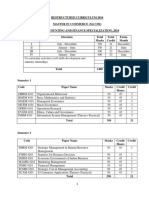
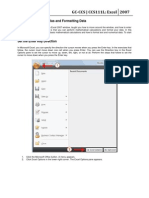
This document provides a cheat sheet on Excel automation using VBA. It covers topics such as opening and saving workbooks, selecting and modifying cells and ranges, formatting cells, working with formulas and functions, creating charts and pivot tables, importing and exporting data, interacting with other applications, handling errors, and more advanced techniques like regression analysis and customizing the user interface. The cheat sheet acts as a reference for common VBA tasks in Excel.
Uploaded by
Widad RachmanCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
140 views6 pagesExcel Automation - Cheatsheet
This document provides a cheat sheet on Excel automation using VBA. It covers topics such as opening and saving workbooks, selecting and modifying cells and ranges, formatting cells, working with formulas and functions, creating charts and pivot tables, importing and exporting data, interacting with other applications, handling errors, and more advanced techniques like regression analysis and customizing the user interface. The cheat sheet acts as a reference for common VBA tasks in Excel.
Uploaded by
Widad RachmanCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 6