0% found this document useful (0 votes)
108 views9 pagesEthics
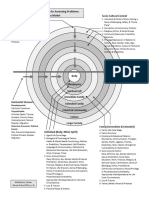
Self-esteem refers to an individual's overall opinion and evaluation of their own self-worth and value. It involves beliefs, feelings, and attitudes that shape one's sense of self and influence various aspects of life. Key features of self-esteem include positive self-perception, self-respect, self-confidence, recognizing inherent self-value, resilience in the face of adversity, self-acceptance, ability to have healthy relationships, and motivation to pursue goals. Self-esteem can be influenced throughout life by experiences and relationships.
Uploaded by
Sourasish NathCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
108 views9 pagesEthics
Self-esteem refers to an individual's overall opinion and evaluation of their own self-worth and value. It involves beliefs, feelings, and attitudes that shape one's sense of self and influence various aspects of life. Key features of self-esteem include positive self-perception, self-respect, self-confidence, recognizing inherent self-value, resilience in the face of adversity, self-acceptance, ability to have healthy relationships, and motivation to pursue goals. Self-esteem can be influenced throughout life by experiences and relationships.
Uploaded by
Sourasish NathCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 9