0% found this document useful (0 votes)
48 views49 pagesUnit 2
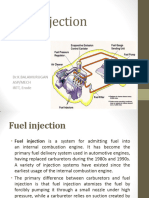
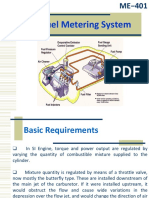
This document discusses fuel systems for internal combustion engines. It begins by describing the components of a carbureted fuel system, including the inlet, venturi throat, floating chamber, and other parts. It then explains the working principles of carburetors and different types. The document also covers fuel pumps, filters, injection systems including multi-point fuel injection and direct injection, and diesel fuel systems including common rail direct injection. Diagrams are provided to illustrate the various fuel system components and their functions.
Uploaded by
A ABHISHEK MARSHALLCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
48 views49 pagesUnit 2
This document discusses fuel systems for internal combustion engines. It begins by describing the components of a carbureted fuel system, including the inlet, venturi throat, floating chamber, and other parts. It then explains the working principles of carburetors and different types. The document also covers fuel pumps, filters, injection systems including multi-point fuel injection and direct injection, and diesel fuel systems including common rail direct injection. Diagrams are provided to illustrate the various fuel system components and their functions.
Uploaded by
A ABHISHEK MARSHALLCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 49