0% found this document useful (0 votes)
93 views8 pagesLaw and Social Transformation in India
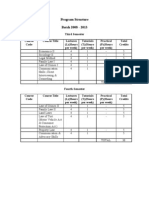
This document outlines the course curriculum for the Semester I LLM program at an unnamed institution. It covers two foundation papers, the first on law and social transformation in India with 4 modules addressing topics like religion and the law, language and the law, community and the law, and modernization and the law. The second foundation paper is on Indian constitutional law and new challenges, with modules on federalism, rights, separation of powers, and democratic processes. It also outlines two group papers in business law, the first on fundamental principles of contract law across 4 modules, and the second on global trade under the World Trade Organization across modules on the WTO agreement, trade in goods, trade in services, and trade related intellectual property.
Uploaded by
jyotibadgeri81Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
93 views8 pagesLaw and Social Transformation in India
This document outlines the course curriculum for the Semester I LLM program at an unnamed institution. It covers two foundation papers, the first on law and social transformation in India with 4 modules addressing topics like religion and the law, language and the law, community and the law, and modernization and the law. The second foundation paper is on Indian constitutional law and new challenges, with modules on federalism, rights, separation of powers, and democratic processes. It also outlines two group papers in business law, the first on fundamental principles of contract law across 4 modules, and the second on global trade under the World Trade Organization across modules on the WTO agreement, trade in goods, trade in services, and trade related intellectual property.
Uploaded by
jyotibadgeri81Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 8