0% found this document useful (0 votes)
27 views6 pagesAssignment in AC
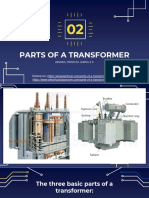
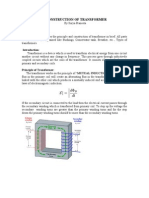
The document describes the key parts and functions of different types of transformers used in power systems. It explains that transformers use magnetic induction to increase or decrease voltage levels for efficient transmission and use of electric power. The main components discussed are the primary and secondary coils, magnetic core, insulation materials, cooling components, and protective devices. Current and potential transformers are also covered as instruments used to measure high voltages and currents in transmission and distribution grids.
Uploaded by
jac obCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
27 views6 pagesAssignment in AC
The document describes the key parts and functions of different types of transformers used in power systems. It explains that transformers use magnetic induction to increase or decrease voltage levels for efficient transmission and use of electric power. The main components discussed are the primary and secondary coils, magnetic core, insulation materials, cooling components, and protective devices. Current and potential transformers are also covered as instruments used to measure high voltages and currents in transmission and distribution grids.
Uploaded by
jac obCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 6