0% found this document useful (0 votes)
49 views6 pagesUnit V Interface and Package
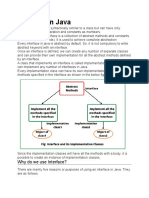
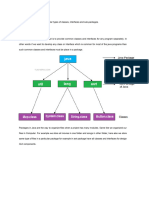
The document discusses interfaces and packages in Java. It defines an interface as a collection of method signatures without implementations that can be used to achieve abstraction and multiple inheritance. Classes can implement multiple interfaces. Packages are used to organize Java code and provide access protection. The key differences between abstract classes and interfaces are that interfaces contain only abstract methods while abstract classes can contain concrete methods, and interfaces support multiple inheritance while abstract classes do not.
Uploaded by
RameshPrasadBhattaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
49 views6 pagesUnit V Interface and Package
The document discusses interfaces and packages in Java. It defines an interface as a collection of method signatures without implementations that can be used to achieve abstraction and multiple inheritance. Classes can implement multiple interfaces. Packages are used to organize Java code and provide access protection. The key differences between abstract classes and interfaces are that interfaces contain only abstract methods while abstract classes can contain concrete methods, and interfaces support multiple inheritance while abstract classes do not.
Uploaded by
RameshPrasadBhattaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 6