0% found this document useful (0 votes)
426 views1 pageGestational Diabetes Management
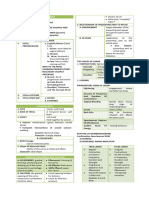
Gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) is a condition where a pregnant woman without diabetes develops high blood sugar levels. It occurs due to insulin resistance associated with pregnancy and is typically diagnosed during the 2nd or 3rd trimester. Risk factors include advanced maternal age, obesity, family history of diabetes, and history of GDM. If left untreated, GDM can lead to complications for both mother and baby such as preeclampsia and macrosomia. Treatment involves glucose monitoring, medical nutrition therapy, and possibly insulin to control blood sugar levels. Proper management of GDM can help prevent adverse outcomes.
Uploaded by
VIAH ANGELA CAASICopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
426 views1 pageGestational Diabetes Management
Gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) is a condition where a pregnant woman without diabetes develops high blood sugar levels. It occurs due to insulin resistance associated with pregnancy and is typically diagnosed during the 2nd or 3rd trimester. Risk factors include advanced maternal age, obesity, family history of diabetes, and history of GDM. If left untreated, GDM can lead to complications for both mother and baby such as preeclampsia and macrosomia. Treatment involves glucose monitoring, medical nutrition therapy, and possibly insulin to control blood sugar levels. Proper management of GDM can help prevent adverse outcomes.
Uploaded by
VIAH ANGELA CAASICopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 1