100% found this document useful (1 vote)
2K views10 pagesLab Report Encoders and Decoders
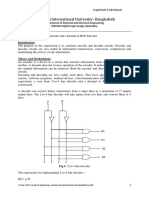
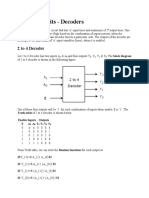
The document describes an experiment to understand and test decoders and encoders. Students implemented a 2-to-4 line decoder and 4-to-2 line encoder using logic gates. They then connected the decoder and encoder in series and verified the input is reproduced, demonstrating their intended functions. Code was also written in Verilog and simulation results matched the expected truth table outputs.
Uploaded by
Owais FarooqCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
100% found this document useful (1 vote)
2K views10 pagesLab Report Encoders and Decoders
The document describes an experiment to understand and test decoders and encoders. Students implemented a 2-to-4 line decoder and 4-to-2 line encoder using logic gates. They then connected the decoder and encoder in series and verified the input is reproduced, demonstrating their intended functions. Code was also written in Verilog and simulation results matched the expected truth table outputs.
Uploaded by
Owais FarooqCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 10