0% found this document useful (0 votes)
28 views32 pagesLecture 2 - Relational Databases
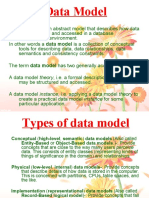
The document discusses data modeling and provides details on conceptual, logical, and physical data modeling. It defines data modeling and explains the process. It also discusses different types of data models and why data modeling is important.
Uploaded by
Bilal AyubCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
28 views32 pagesLecture 2 - Relational Databases
The document discusses data modeling and provides details on conceptual, logical, and physical data modeling. It defines data modeling and explains the process. It also discusses different types of data models and why data modeling is important.
Uploaded by
Bilal AyubCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 32