0% found this document useful (0 votes)
626 views78 pagesBiological Classification Guide
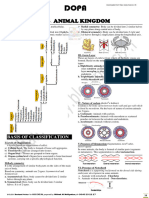
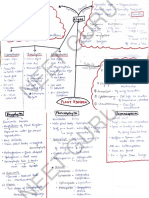
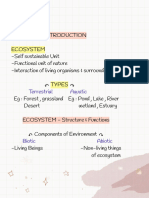
The document discusses the classification of biological organisms from early non-scientific to modern scientific classification systems. It covers the key people and systems involved like Aristotle, Linnaeus, Haeckel, Whittaker, and Woese. It also provides details on the classification of fungi and characteristics of the major fungal groups.
Uploaded by
subu231201Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
626 views78 pagesBiological Classification Guide
The document discusses the classification of biological organisms from early non-scientific to modern scientific classification systems. It covers the key people and systems involved like Aristotle, Linnaeus, Haeckel, Whittaker, and Woese. It also provides details on the classification of fungi and characteristics of the major fungal groups.
Uploaded by
subu231201Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 78