100% found this document useful (1 vote)
67 views63 pagesCloud Computing
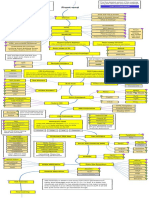
The document discusses cloud computing and data centers. It covers topics like cloud stacks, service models, types of clouds, infrastructure, servers, racks, blades, data center components, communication in data centers, utilization, and power. The goal of clouds is to maximize resource utilization and allow applications to dynamically scale their resource needs.
Uploaded by
1902023abidamubdiCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
100% found this document useful (1 vote)
67 views63 pagesCloud Computing
The document discusses cloud computing and data centers. It covers topics like cloud stacks, service models, types of clouds, infrastructure, servers, racks, blades, data center components, communication in data centers, utilization, and power. The goal of clouds is to maximize resource utilization and allow applications to dynamically scale their resource needs.
Uploaded by
1902023abidamubdiCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 63