0% found this document useful (0 votes)
18 views11 pages04a Array
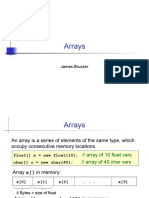
The document discusses Java arrays including declaring array variables, processing arrays, passing arrays to methods, and ArrayLists. Arrays are fixed-length containers that hold values of a single type. Arrays are declared with a size and elements accessed via indexes. For/for-each loops are commonly used to process array elements. When passing arrays to methods, the reference is copied so changes within the method affect the original array.
Uploaded by
yawner9304Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
18 views11 pages04a Array
The document discusses Java arrays including declaring array variables, processing arrays, passing arrays to methods, and ArrayLists. Arrays are fixed-length containers that hold values of a single type. Arrays are declared with a size and elements accessed via indexes. For/for-each loops are commonly used to process array elements. When passing arrays to methods, the reference is copied so changes within the method affect the original array.
Uploaded by
yawner9304Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 11