0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views3 pagesTypes of Data
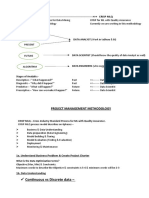
The document discusses two main types of data: qualitative and quantitative data. Qualitative data consists of categories or types of attributes, while quantitative data is based on counting or measuring. Quantitative data can be further broken down into discrete and continuous data, with discrete data taking a limited set of values and continuous data having precision limited only by measurement.
Uploaded by
quasideus19Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views3 pagesTypes of Data
The document discusses two main types of data: qualitative and quantitative data. Qualitative data consists of categories or types of attributes, while quantitative data is based on counting or measuring. Quantitative data can be further broken down into discrete and continuous data, with discrete data taking a limited set of values and continuous data having precision limited only by measurement.
Uploaded by
quasideus19Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 3