BASICS OF RFID TECHNOLOGY
Pramod Bhat M Pavan Kumar P N
�History of RFID
Invented in 1948 by Harry Stockman. Initial application was during World War II-The United
Kingdom used RFID devices to distinguish returning English airplanes from inbound German ones. RADAR was only able to signal the presence of a plane. Came into commercial use only in 1990s.
�Components of RFID
An RFID tag is an object that can be stuck on or incorporated into a
product, animal, or person for the purpose of identification using radio waves . Tags ( Chip + Antenna + Substrate ). Tag types -Active. -Passive. -Read only. -Write only . Frequency at which these tags are used -Between 125 to 134 kilohertz. -At 13.56 megahertz. -Between 868 to 956 megahertz. -At 2.45 gigahertz.
�Components of RFID
�Passive RFID Tags
Tag contains an antenna, and a small chip
that stores a small amount of data Tag can be programmed at manufacture or on installation Tag is powered by the high power electromagnetic field generated by the antennas usually in doorways The field allows the chip/antenna to reflect back an extremely weak signal containing the data. Collision Detection recognition of multiple tags in the read range is employed to separately read the individual tags
�Active RFID Tags
Battery Powered Tags
Have much greater range 100m
Hold much more information
Kbytes Can integrate sensing technology
Temperature, GPS
Can signal at defined time Multiple tags can be recorded at
once
�Active RFID v/s Passive RFID
Active RFID Tag Power Source Internal to tag Passive RFID Energy transferred using RF from reader No Only in field of reader Very High
Tag Battery Availability of power Required signal strength to Tag
Yes Continuous Very Low
Range
Multi-tag reading
Up to 100m
1000s of tags recognized up to 100mph Up to 128Kb or read/write with sophisticated search and access
Up to 3-5m, usually less
Few hundred within 3m of reader 128 bytes of read/write
Data Storage
�Components of RFID
Interrogator (Antenna + Reader) : They are used to read
the tags and in certain cases even remotely writes to the tag. Middleware: Middleware is the needed interface between the existing company databases and information management software. Business Application Software: used to manage the collected data. Middleware provides a range of functions:
Data filtering System monitoring Multiple reader coordination
�Electronic Product Code (EPC)
Each tag consists a unique code that facilitates
identification process known as EPC E.g. 613.23000.123456.123456789 (96 bits) Header- defines version of EPC (8 bits) EPC Manager- Describes product Manufacturer (24 bits) Object Class- Describes Product Type (24 bits) Serial Number- Unique ID for that product item (36 bits)
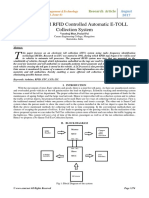
�System Overview
�How RFID Works
PC
Time DATA FLOW RFID-READER RF COUPLING
Up-to-date
RFID-TAG
Energy
PERSONALIZER (Application Device)
RFID system
�Range and Speed of RFID
Frequency 125-150 kHz Regulation Basically unregulated ISM band, differing power levels and duty cycle Non-specific Short Range Devices (SRD), Location Systems ISM band (Region 2); increasing use in other regions, differing power levels and duty cycle ISM band, differing power levels and duty cycle Range 10 cm Data Speed Low Low to moderate Moderate Comments Animal identification and factory data collection systems Popular frequency for I.C. Cards (Smart Cards) Asset tracking for U.S. DoD (Pallets) EAN.UCC GTAG, MH10.8.4 (RTI), AIAG B-11 (Tires) IEEE 802.11b, Bluetooth, CT, AIAG B-11
13.56 MHz
< 1m 1 100 m
433 MHz
860-930 MHz
25m
Moderate to high
2450 MHz
12m
High
�Benefits of RFID
Read/Write
- Ability to add information directly to tags enables each unique asset to carry its own unique history Non-contact Reads - Ability to read tags at a distance, under a variety of environmental conditions, without physical manipulation of the asset Fast Read - Ability to simultaneously read large numbers (10001750 tags/sec) of items Automation - Requires less human intervention Authenticity - Each RFID chip is unique and can not be replicated
�RFID v/s Barcode
RFID Forging is difficult Barcode Forging is easy Scanner not required. No need Scanner needs to see the bar to bring the tag near the code to read it reader RFID is comparatively fast Can read multiple tags Can read only one tag at a time
Relatively expensive as compared to Bar Codes (Reader 1000$, Tag 20 cents a piece) - EPC
Inexpensive - UPC
Can be reusable within factory Cannot be reused premises
�Case Study - Gillette & Co:
Objective: To Track movement of product from Packaging
Center to Plants distribution center.
Previously->Using Bar Code, time taken=80 sec to 20 min
1999->With RFID it takes 20 seconds.
Gains->Gillette saves 20% in Operational Cost at each
Distribution Center.
�Namma Metro
RFID Tokens Contactless RFID Smart Cards
�RFID Radar
Identifying RFID transponders in its zone Measure the range and direction of those transponders from the reader antennas.
�Advantages of RFID Radar
This technology brings conventional RFID and RTLS
technology closer together. This technology encourages the development of longer range transponder technology to allow operation out to 100 meters Allows solution of complex security situations, such as when a transponder crosses a fictitious boundary - like cattle moving out of a field or trolleys from a carpark. Allows single radars to monitor much larger zones than multiple RFID systems.
�THANK YOU
Any Questions?