Objectives
The basic concepts associated with the EntityRelationship (ER) model, a high-level conceptual data model. A diagrammatic technique for displaying an ER model. How to identify problems called connection traps, which may occur when creating an ER model.
2
Entity-Relationship Modeling
Concepts of the ER Model
Entity Type
Entity types Relationship types Attributes
Entity Type An object or concept that is identified by the enterprise as having an independent existence. Entity An object or concept that is uniquely identifiable.
4
Examples of Entity Types
Examples of Entity
�Entity Type
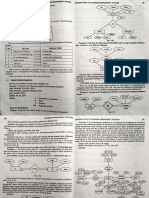
Diagrammatic Representation of Strong and Weak Entity Types
Strong Entity Type (parent, owner, dominant)
An entity type that is not existencedependent on some other entity type.
Weak Entity Type
Weak Entity Type (child, dependent, subordinate)
An entity type that is existence-dependent on some other entity type.
7
Strong Entity Type
10
Relationship Types
Diagrammatic Representation Relationship Type
of
Relationship Type
A meaningful association among entity types.
Relationship
An association of entities where the association includes one entity from each participating entity type.
9 10
Diagrammatic Representation Weak Relationship Type
Staff
of
Degree of a Relationship
Degree of a Relationship
The number of participating entities in a relationship.
Related to
The entities involved in a particular relationship are referred to as participants. The number of participants in a relationship is called the degree.
11 12
Next_of_Kin
�Binary Relationship called Owns
Ternary Relationship called SetsUp
13
Quaternary Relationship called Arranges
Recursive (Unary) Relationship
Recursive Relationship
A relationship where the same entity participates more than once in a different roles.
24
16
Recursive Relationship called Supervises
Recursive (Unary) Relationship
Role name
To indicate the purpose that each participating entity play in a relationship
17
18
�Entities associated through two distinct Relationships
Attributes
Attribute
A property of an entity or a relationship type.
19
20
Examples of Attribute Attributes
Attribute Domain
A set of values that may be assigned to a single-valued attribute.
21
22
Examples of Attribute Domain
Attribute Domain : 9000 -30000
Types of Attributes
Simple Attribute vs. Composite Attribute Single-Valued Attribute vs. MultiValued Attribute Derived Attribute
23
24
�Attributes
Attributes
Simple Attribute
An attribute composed of a single component with an independent existence. Cannot be further subdivided as a meaningful information. Ex. Sex, Salary
Composite Attribute
An attribute composed of multiple components each with an independent existence. Can be further divides. Ex. Address can be divided into Street#, City, State, Zip
25
26
Attributes
Attributes
Single-valued Attribute
An attribute that holds a single-value for a single entity. Customer#, Branch#
Multi-valued Attribute
An attribute that holds multiple values for a single entity. Tel_No : 234-5678 and 456-7839
27
28
Attributes
Diagrammatic Representation of Attributes
Multi-value attribute SAddress SName Position
Derived Attribute
An attribute that represents a value that is derivable from the value of a related attribute or set of attributes, not necessarily in the same entity. Age attribute might be derived from DOB (Date of Birth) attribute
29
DOB
Staff
Tel_No NIN
Sex Staff_No Derived attribute
Age
Salary
30
�Types of Key
Keys
Candidate Key Candidate Key
An attribute or set of attributes that uniquely identifies individual occurrences of an entity type. Staff: Staff_No, >>>>>
Primary Key Composite Key
31
32
Diagrammatic Representation of Attributes
SAddress SName Position
Keys
Candidate Key
An attribute or set of attributes that uniquely identifies individual occurrences of an entity type. Staff: Staff_No, NIN (National Insurance Number), SName+Tel_No, SName+DOB
DOB
Staff
Tel_No NIN
Sex Staff_No
Age
Salary
33 34
Keys
Keys
Primary Key
The candidate key selected to be a primary key The consideration is based on: attribute length (minimal) current and future certainty of uniqueness Staff_No
35
Composite Key
A candidate key that consists of two or more attributes. Staff: SName+Tel_No, SName+DOB
36
�Diagrammatic Representation of Primary Key
SAddress SName Position
Attribute on Relationships
A relationship can also has its own attribute. The presence of one or more attributes assigned to a relationship may indicate that the relationship conceals an unidentified entity. For example, the presence of the Date_View and Comments attributes on the Views relationship may indicate the presence of an entity called Viewing
38
DOB
Staff
Tel_No
Sex Staff_No Primary Key
NIN
Age
Salary
37
Relationship called Views with attributes
Diagrammatic Representation of Entities, Relationships, and Primary Key Attributes
39
40