Khulna Khan Bahadur Ahsanullah University
Department of CSE
Course Title: Object Oriented Programming
Course Code: CSE 061 1203
Week - 07
Class – 01
1. What is Access Modifiers?
The access modifiers in Java specifies the accessibility or scope of a field,
method, constructor, or class.
There are two types of modifiers in Java: access modifiers and non-access
modifiers.
We can change the access level of fields, constructors, methods, and class by
applying the access modifier on it.
2. Discuss different types of access modifiers.
There are four types of Java access modifiers:
a. Private: The access level of a private modifier is only within the class. It
cannot be accessed from outside the class.
b. Default: The access level of a default modifier is only within the package. It
cannot be accessed from outside the package. If you do not specify any access
level, it will be the default.
c. Protected: The access level of a protected modifier is within the package and
outside the package through child class. If you do not make the child class, it
cannot be accessed from outside the package.
1|Page
� d. Public: The access level of a public modifier is everywhere. It can be accessed
from within the class, outside the class, within the package and outside the
package.
There are many non-access modifiers, such as static, abstract, synchronized, native,
volatile, transient, etc. Here, we are going to learn the access modifiers only.
Understanding Java Access Modifiers
Access within within outside package by outside
Modifier class package subclass only package
Private Y N N N
Default Y Y N N
Protected Y Y Y N
Public Y Y Y Y
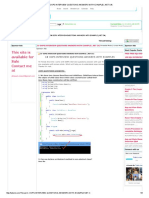
a. Private
The private access modifier is accessible only within the class. In this example, we
have created two classes A and Simple. A class contains private data member and
private method. We are accessing these private members from outside the class, so
there is a compile-time error.
1. class A{
2. private int data=40;
3. private void msg(){System.out.println("Hello java");}
2|Page
� 4. }
5.
6. public class Simple{
7. public static void main(String args[]){
8. A obj=new A();
9. System.out.println(obj.data);//Compile Time Error
10. obj.msg();//Compile Time Error
11. }
12.}
Role of Private Constructor
If you make any class constructor private, you cannot create the instance of that class
from outside the class. For example:
1. class A{
2. private A(){}//private constructor
3. void msg(){System.out.println("Hello java");}
4. }
5. public class Simple{
6. public static void main(String args[]){
7. A obj=new A();//Compile Time Error
8. }
9. }
Note: A class cannot be private or protected except nested class.
3|Page
�b. Default
If you don't use any modifier, it is treated as default by default. The default modifier
is accessible only within package. It cannot be accessed from outside the package.
It provides more accessibility than private. But, it is more restrictive than protected,
and public.
Example of default access modifier
In this example, we have created two packages pack and mypack. We are accessing
the A class from outside its package, since A class is not public, so it cannot be
accessed from outside the package.
1. //save by A.java
2. package pack;
3. class A{
4. void msg(){System.out.println("Hello");}
5. }
1. //save by B.java
2. package mypack;
3. class B{
4. public static void main(String args[]){
5. A obj = new A();//Compile Time Error
6. obj.msg();//Compile Time Error
7. }
8. }
In the above example, the scope of class A and its method msg() is default so it
cannot be accessed from outside the package.
4|Page
� Class – 02
c. Protected
The protected access modifier is accessible within package and outside the
package but through inheritance only.
The protected access modifier can be applied on the data member, method and
constructor. It can't be applied on the class.
It provides more accessibility than the default modifier. In this example, we
have created the two packages pack and my pack. The A class of pack package
is public, so can be accessed from outside the package. But msg method of
this package is declared as protected, so it can be accessed from outside the
class only through inheritance.
1. //save by A.java
2. package pack;
3. public class A{
4. protected void msg(){System.out.println("Hello");}
5. }
1. //save by B.java
2. package mypack;
3. import pack.*;
4. class B extends A{
5. public static void main(String args[]){
6. B obj = new B();
7. obj.msg();
8. }
9. }
Output: Hello
5|Page
�d. Public
The public access modifier is accessible everywhere. It has the widest scope among
all other modifiers.
Example of public access modifier
1. //save by A.java
2. package pack;
3. public class A{
4. public void msg(){System.out.println("Hello");}
5. }
1. //save by B.java
2.
3. package mypack;
4. import pack.*;
5.
6. class B{
7. public static void main(String args[]){
8. A obj = new A();
9. obj.msg();
10. }
11.}
Output: Hello
6|Page
�Java Access Modifiers with Method Overriding
If you are overriding any method, overridden method (i.e. declared in subclass) must
not be more restrictive.
1. class A{
2. protected void msg(){System.out.println("Hello java");}
3. }
4.
5. public class Simple extends A{
6. void msg(){System.out.println("Hello java");}//C.T.Error
7. public static void main(String args[]){
8. Simple obj=new Simple();
9. obj.msg();
10. }
11.}
The default modifier is more restrictive than protected. That is why, there is a
compile-time error.
7|Page
�Non-Access Modifiers
These types of modifiers are used to control a variety of things, such as inheritance
capabilities, whether all objects of our class share the same member value or have
their own values of those members, whether a method can be overridden in a
subclass, etc.
A brief overview of these modifiers can be found in the following table:
Modifier
Overview
Name
static The member belongs to the class, not to objects of that class.
Variable values can't be changed once assigned, methods can't be overridden
final
classes can't be inherited.
If applied to a method - has to be implemented in a subclass, if applied to a
abstract
class - contains abstract methods
synchronized Controls thread access to a block/method.
The variable value is always read from the main memory, not from a specific
volatile
thread's memory.
transient The member is skipped when serializing an object.
Class – 03
Class Test
8|Page