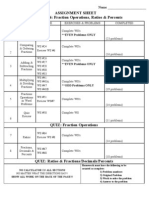
ity
rs
ve
y
op
ni
U
C
ge
w
Chapter 1: Reviewing number concepts
ie
id
ev
br
am
-R
-C
s
es
Key words
y
Pr
op
• Natural number
•
ity
C
Integer
•
rs
w
Prime number
•
ie
ve
Symbol
y
•
ev
Multiple
op
ni
• Factor
R
C
• Composite numbers
ge
w
Prime factor
•
ie
id
Square
•
ev
br
Square root
•
am
Cube
-R
• Directed numbers
-C
•
s
BODMAS
es
y
Pr
op
ity
In this chapter you
C
will learn how to:
rs
w
•
ie
ve
identify and classify
y
different types of numbers
ev
op
ni
• find common factors and
R
common multiples of
C
numbers
ge
• write numbers as products
ie
id
of their prime factors
ev
br
• calculate squares, square
am
-R
roots, cubes and cube roots
of numbers
•
-C
work with integers used in
s
es
real-life situations
•
y
revise the basic rules for
Pr
op
operating with numbers
• perform basic calculations This statue is a replica of a 22 000-year-old bone found in the Congo. The real bone is only 10 cm long and it
ity
C
using mental methods and is carved with groups of notches that represent numbers. One column lists the prime numbers from 10 to 20.
rs
w
with a calculator. It is one of the earliest examples of a number system using tallies.
ie
ve
y
ev
op
ni
Our modern number system is called the Hindu-Arabic system because it was developed by
R
Hindus and spread by Arab traders who brought it with them when they moved to different
e
places in the world. The Hindu-Arabic system is decimal. This means it uses place value based
w
g
on powers of ten. Any number at all, including decimals and fractions, can be written using
ie
id
place value and the digits from 0 to 9.
ev
br
am
-R
-C
Unit 1: Number 1
s
es
Copyright Material - Review Only - Not for Redistribution