Booting Linux
Chanik Park cipark@postech.edu
2004
1/16
CS 512 Advanced Operating System
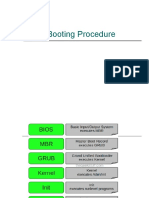
�Booting Process Overview
Based on IA32 architecture Six stages
BIOS selects the boot device BIOS loads the bootsector from the boot device Linux bootsector (arch/i386/boot/bootsect.S) LILO (or other bootloaders) bootsector Bootsector loads setup, decompression routines and compressed kernel image The kernel is uncompressed in protected mode Low-level initialization is performed by asm code High-level C initialization
2004
2/16
CS 512 Advanced Operating System
�Boot Process Overview (Cont)
2004
3/16
CS 512 Advanced Operating System
�Boot Loaders
Operation
decide what to load (by prompting user). load kernel and possibly additional data, such as initrd or parameters for kernel (retrieved from firmware or boot command line). set up an execution environment suitable for kernel (e.g., put CPU in privileged mode). run kernel.
2004
4/16
CS 512 Advanced Operating System
�Taxonomy
Specialized loaders : LinuxBIOS, syslinux, Netboot General loaders running under another operating system : LOADLIN, ArLo File system aware general loaders running on firmware : Shoelace (Minix FS), GRUB, SILO File system unaware general loaders running on firmware : LILO requires map installer (/sbin/lilo)
2004
5/16
CS 512 Advanced Operating System
�FS-Aware vs FS-Unaware Boot Loaders
Standard Linux FS ? GRUB
2004 6/16
few change in boot loader/map installer LILO
CS 512 Advanced Operating System
�Evolution of standard Linux file system vs bootloader (FS-aware ?)
Shoelace LILO GRUB New LILO ?
time
2004
7/16
CS 512 Advanced Operating System
�i386 Dependency
1024 cylinder limit (due to BIOS)
LILO uses BIOS for all disk operations EDD (Enhanced Disk Drive Spec) in 1995 Support for EDD added to LILO in 1999
Memory size limit
1MB due to real mode : 4+16 bit address space (Image) compressed kernel (zImage) bigger kernel (bzImage) 16MB due to 8+16 protected mode (i286) 64MB due to BIOS
2004
8/16
CS 512 Advanced Operating System
�Loading bzImage
2004
9/16
CS 512 Advanced Operating System
�Adding New Features ?
where ? in boot loader or in the kernel Situation
large # of architectures and a large # of boot loaders per architecture
So, changes in boot loaders are not likely to be feasible. Then, extensions of boot process within the kernel.
Be architecture-independent !
2004
10/16
CS 512 Advanced Operating System
�Root File System for Kernel
Operations
Mount root file system Need to know where it is. Need driver to access the media. Run user-space programs Early days : a set of pre-compiled kernels containing only a small number of drivers each (due to conflicting drivers) load module chosen by user ? Now : let the boot loader load kernel modules Initial RAM disk called initrd : a single file to make the work of boot loader simple
11/16 CS 512 Advanced Operating System
Loading drivers into kernel ?
2004
�initrd
Usage either for regular root file system or as an intermediate environment before switching to real root file system : run /linuxrc before switching Main limitation Memory for initrd file, RAM disk, any other data kernel needs at that time, and kernel Thus, the size of compressed initrd ~ 1/3 of memory not occupied by kernel (see figure)
12/16 CS 512 Advanced Operating System
2004
�Changing root file system
Q : changing a carpet while standing on it ? A1 : jump up change_root A2 : roll out a new one next to the old one and walk over pivot_root other ?
2004
13/16
CS 512 Advanced Operating System
�Ultimate Boot Loader
An ultimate boot loader can be made to access any resources the kernel can access
Kernel itself can access any resources. many file systems, RAID, TCP/IP, NFS, SMB, DHCP, HTTP, Whats missing ? A method to boot a Linux kernel from within Linux bootimg LOBOS Two Kernel Monte Etc. * Assignment #1 : report on bootimg, LOBOS, (1 week)
LinuxBIOS : put Linux kernel in flash EPROM (feature-rich boot loader)
2004 14/16 CS 512 Advanced Operating System
�Evolution of Boot Concepts
The humble beginning (1991)
Linux boots stand-alone from floppy Shoelace is used to boot from Minix filesystem on hard disk 1992 LILO (from any) / BOOTLIN (from DOS) 1994 LOADLIN replaces BOOTLIN / SYSLINUX reads FAT floppies 1995 GRUB, a modern FS-aware boot loader 1991 root FS device can be set in kernel image 1995 NFS root mounts root FS from NFS server 1996 initial RAM disk support added to kernel / change_root mechanism 2000 pivot_root / union root mount / early freeing of initrd memory pages
15/16 CS 512 Advanced Operating System
Beyond Minix (1992 ~ 1995)
Root file system abstraction (1991 ~ 2000)
2004
�Kernel image abstraction
1996 Netboot boots from Ethernet, using TFTP 1999 GRUB supports TFTP boot 2000 Linux boots Linux / LinuxBIOS
2004
16/16
CS 512 Advanced Operating System