ME4219 - INDUSTRIAL PLANT ENGINEERING
Miranda, Neil Paolo T.
Refrigeration Systems Terms
1. Refrigerant - A fluid used in refrigeration systems to absorb and release heat, typically in a cyclic
process. Common examples include R-134a and R-410A.
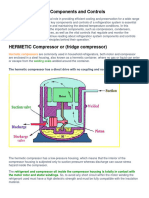
2. Compressor - A component that compresses the refrigerant, increasing its pressure and temperature
before it moves to the condenser.
3. Condenser- A heat exchanger where the refrigerant releases its absorbed heat to the surrounding
environment, typically changing from a gas to a liquid.
4. Evaporator - A heat exchanger where the refrigerant absorbs heat from the environment, causing it to
evaporate from a liquid to a gas.
5. Expansion Valve - A device that regulates the flow of refrigerant into the evaporator, reducing its
pressure and temperature.
6. Capillary Tube- A type of expansion device that controls refrigerant flow based on pressure drop
through a small-diameter tube.
7. Heat Exchanger - A system or device that transfers heat between two or more fluids or gases.
8. Thermostat - A control device that regulates the temperature by turning the refrigeration system on
or off based on a set temperature.
9. Refrigerant Cycle - The process through which refrigerant absorbs and releases heat, including
compression, condensation, expansion, and evaporation.
�10. Subcooling - The process of cooling a refrigerant below its condensation temperature to increase
system efficiency.
11. Superheating - Heating a refrigerant above its boiling point in the evaporator to ensure it is
completely in gas form before entering the compressor.
12. Accumulator- A component that collects and stores excess refrigerant vapor from the evaporator to
prevent liquid refrigerant from entering the compressor.
13. Receiver - A storage tank that holds the refrigerant liquid after it exits the condenser and before it
reaches the expansion valve.
14. Evaporator Coil - The coil in the evaporator where the refrigerant absorbs heat from the surrounding
air or fluid.
15. Condenser Coil - The coil in the condenser where the refrigerant releases heat to the surrounding
environment.
16.Pressure Switch - A device that monitors the pressure within the refrigeration system and activates or
deactivates components to maintain proper pressure levels.
17. Compressor Oil- Lubricating oil used in the compressor to reduce friction and wear on moving parts.
18. Refrigerant Charge- The amount of refrigerant within a refrigeration system, crucial for proper
system operation.
19. Heat Pump - A device that can reverse the refrigeration cycle to provide heating as well as cooling by
moving heat from one place to another.
�20. Desuperheater- A component that captures and utilizes the excess heat from the refrigerant after
compression before it enters the condenser.
21. Air-Cooled Condenser - A type of condenser that uses ambient air to cool the refrigerant, typically
through a fan.
22. Water-Cooled Condenser - A type of condenser that uses water to absorb heat from the refrigerant,
often found in larger systems.
23. Dual Evaporator System - A system with two separate evaporators for different temperature zones
or applications.
24. Refrigerant Leak Detector- A device used to identify and locate leaks in a refrigeration system to
prevent refrigerant loss.
25. Condensate Drain - A system for removing water that forms from condensation in the evaporator or
other parts of the refrigeration system.
26.Heat Exchange Efficiency - A measure of how effectively heat is transferred between fluids or gases in
the heat exchangers.
27. Cycle Time- The time it takes for a refrigeration cycle to complete one full process of compression,
condensation, expansion, and evaporation.
28. Flash Gas - The refrigerant gas that forms when liquid refrigerant experiences a sudden drop in
pressure.
�29. Pressure-Temperature Chart- A graphical representation showing the relationship between the
pressure and temperature of a refrigerant.
30. Suction Line - The line that carries refrigerant vapor from the evaporator to the compressor.
31. Discharge Line - The line that carries high-pressure refrigerant gas from the compressor to the
condenser.
32. Freezing Point - The temperature at which a refrigerant changes from a liquid to a solid, important
for selecting appropriate refrigerants.
33. Defrost Cycle - A process used to remove ice buildup from the evaporator coils, ensuring efficient
heat exchange.
34. Thermal Expansion Valve (TXV) - A device that regulates the refrigerant flow based on the
temperature and pressure of the evaporator.
35. Refrigerant Recovery- The process of capturing and storing refrigerant from a system during
maintenance or repair to prevent environmental release.
36. Chiller- A refrigeration system designed specifically to cool large quantities of water for industrial or
commercial use.
37. Unitary System - A type of refrigeration system that includes all necessary components in a single
package, often used in residential and small commercial applications.
38. Packaged System - A complete refrigeration system with all components housed in a single unit,
used for cooling or heating in various applications.
�39. Superheat - The temperature rise of a refrigerant vapor above its saturation temperature after all
the liquid has evaporated.
40. Subcooling - The process of cooling refrigerant below its condensation temperature to increase its
density and improve system efficiency.
41. Cooling Load - The amount of heat that must be removed from a space to maintain a desired
temperature, influencing system size and capacity.
42. Heating Load - The amount of heat that must be added to a space to maintain a desired
temperature, affecting system design and operation.
43. Air Handler - A device that circulates air through a building, often including components like
evaporator coils and fans.
44. Reciprocating Compressor - A type of compressor that uses pistons and cylinders to compress
refrigerant gas.
45. Scroll Compressor - A type of compressor that uses spiral-shaped elements to compress
refrigerant gas, known for its efficiency and quiet operation.
46. Rotary Compressor - A type of compressor with rotating elements that compress refrigerant, often
used in smaller systems.
47. Accumulator - A device that stores refrigerant vapor and ensures that only vapor enters the
compressor to prevent liquid slugging.
48. Heat Exchanger Efficiency - A measure of how effectively heat is transferred between two fluids or
gases in a heat exchanger.
�49. Vapor Compression Cycle - The process used by most refrigeration systems where refrigerant
undergoes compression, condensation, expansion, and evaporation to transfer heat.
50. Temperature Differential - The difference in temperature between the refrigerant in the
evaporator and the surrounding environment, affecting system efficiency and performance.