Dipesh Thakur
Table of commands and description used during the practical:
S.N Commands Description
.
1. hostname <hostname> This command allows us to change the name
of the device.
2. enable password <password> This command allows us to secure the
privileged-exec mode with a password.
3. line console 0 These commands help us to secure the
password <password> user-exec mode with a secure password.
login
4. line vty 0 <1-?> These commands enable a secure medium of
password <password> telnet and ssh which is protected by password.
login
5. service password-encryption This command encrypts the passwords so that
it is hard to discern the actual password by just
about anybody by using ‘show running-config’.
6. banner motd <prompt> Using this command, a message can be
displayed whenever a networking device is
accessed.
7. copy running-config Both of these commands do the same
startup-config,write thing;i.e., copy the commands in NVRAM of
the device so that they don’t get erased when
device is booted.
8. ip dhcp pool <pool_name> These commands are used to create a dhcp
network <ip address> <subnet-mask> server for automatic ip address assignment.
default-router <ip address>
9. ip dhcp excluded-address This command helps us to exclude ip
<beginning ip> <ending ip> addresses from dhcp server.
According to the reference provided by the assignment guideline, I have created a network
topology for the assignment. The topology is given below:
1
�Dipesh Thakur
figure:Network Topology
In Switch0, following commands were entered:
Switch>enable
Switch#config terminal
Switch(config)#hostname Texas-SW1
Texas-SW1(config)#enable password class
Texas-SW1(config)#line console 0
Texas-SW1(config-line)#password Texas
Texas-SW1(config-line)#login
Texas-SW1(config-line)#exit
Texas-SW1(config)#line vty 0 15
Texas-SW1(config-line)#password cisco
Texas-SW1(config-line)#login
Texas-SW1(config-line)#exit
Texas-SW1(config)#banner motd #Warning! Authorized Access Only!#
Texas-SW1(config)#service password-encryption
Texas-SW1(config)#end
Texas-SW1#write
The commands entered in CLI of Switch0 allows network administrators to protect the
various interfaces (user-exec mode, privileged-exec mode, etc.) from unauthorized access.
2
�Dipesh Thakur
A banner message is displayed at the start to notify anyone on the same matter. The
commands are saved in NVRAM of the switch to protect against erosion.
Results of the following commands are as follows:
As we can see from the above screenshot, the various modes of the switch are secured by
passwords to prevent unauthorized access. A banner message is promptly displayed to
inform about the access regulation as well.
Using ‘show running-config’ command in privileged-exec mode we can see that name of the
switch has been changed according to the instructions and passwords have been encrypted
as well.
In Switch1, following commands were entered:
Switch>enable
Switch#config terminal
Switch(config)#hostname Texas-SW1
Texas-SW2(config)#enable password class
Texas-SW2(config)#line console 0
Texas-SW2(config-line)#password Texas
Texas-SW2(config-line)#login
Texas-SW2(config-line)#exit
3
�Dipesh Thakur
Texas-SW2(config)#line vty 0 15
Texas-SW2(config-line)#password cisco
Texas-SW2(config-line)#login
Texas-SW2(config-line)#exit
Texas-SW2(config)#banner motd #Warning! Authorized Access Only!#
Texas-SW2(config)#service password-encryption
Texas-SW2(config)#end
Texas-SW2#write
The commands entered in CLI of Switch1 allows network administrators to protect the
various interfaces (user-exec mode, privilege-exec mode, etc.) from unauthorized access. A
banner message is displayed at the start to notify anyone on the same matter. The
commands are saved in NVRAM of the switch to protect against erosion.
Results of the following commands:
Due to necessary measures to secure various modes in Switch1, we can see that
unauthorized people can’t access the switch.
Using the ‘show running-config’ command in privileged-exec mode, we can see that the
name of the switch has been changed properly and passwords have been encrypted as well.
In Router0, following commands were entered:
4
�Dipesh Thakur
Router>enable
Router#config terminal
Router(config)#hostname Texas-Router
Texas-Router(config)#enable password class
Texas-Router(config)#line console 0
Texas-Router(config-line)#password Texas
Texas-Router(config-line)#login
Texas-Router(config-line)#exit
Texas-Router(config)#line vty 0 15
Texas-Router(config-line)#password Texas
Texas-Router(config-line)#login
Texas-Router(config-line)#exit
Texas-Router(config)#service password-encryption
Texas-Router(config)#banner motd #Warning! Authorized Access Only!#
Texas-Router(config)#ip dhcp pool Texas-BIT
Texas-Router(dhcp-config)#network 192.168.1.0 255.255.255.0
Texas-Router(dhcp-config)#default-router 192.168.1.1
Texas-Router(dhcp-config)#exit
Texas-Router(config)#ip dhcp excluded-address 192.168.1.2 192.168.1.10
Texas-Router(config)#interface g0/0
Texas-Router(config-if)#ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0
Texas-Router(config-if)#no shutdown
Texas-Router(config-if)#end
Texas-Router#write
Following commands allows network administrators to protect against unauthorized access
in various interfaces (user-exec mode, privileged-exec mode etc). A message is displayed to
inform anyone about the same. A dhcp server is also created to enable automatic ip
assignment on devices. Few ip addresses are excluded as well.
Result of the following commands:
As the picture suggests, the user-exec mode and privileged-exec mode are secured.
5
�Dipesh Thakur
Using the do show running-config command in global configuration mode we can see that
hostname has been appropriately changed and passwords are encrypted as well. A DHCP
server with proper configuration has been created as well.
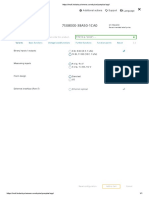
As we can see, the dhcp server is working properly and with the use of it, we get assigned
an ip address automatically.