DQ2-9 : What are the advantages and disadvantages of using the accrual basis of
accounting rather than the cash basis?
Advantages of accrual basis :
● More accurate depiction of financial situation of an organization since revenues
are recorded when they are earned and expenses are recorded when they are
incurred
● More useful for making financial decisions for users because the info they
provide is more transparent than with cash basis
Disadvantages of accrual basis :
● It can be more challenging to implement than cash basis
○ In cash basis, you simply record transaction based on the cash in/outflow
○ In accrual basis, several processes like the five step process for revenue
recognition have to be used to determine whether or not to record a
transaction
● Having to pay taxes on income you haven’t even received yet on hand because
sales are reported when they are earned
AP2-3B : For each of the following transactions, indicate the effect on the basic
accounting equation (Assets = Liabilities + Shareholders’ Equity) -
Purchase of equipment for cash. (Credit Cash, Debit Equipments - all in assets)
Receipt of a loan from a bank. (Credit Loan Payable, Debit Cash - Assets & Liabilities)
Purchase of inventory on account. (Debit Inventory, Credit Accounts Payable - A & L)
Sale of services to a customer for cash. (Debit Cash, Credit Retained Earnings as
Revenue - A & SE)
Payment of account payable. (Credit Cash, Debit Account Payable - A & L)
f) Recorded wages owed to employees. (Debit Retained Earnings as Wages Expense,
Credit Wages Payable - L & SE)
Payment of interest on loan. (Credit Cash, Debit Retained Earnings as Interest Expense
- A & SE)
Repayment of loan principal. (Credit Cash, Debit Loan Payable - A & L)
Payment of wages owed to employees that were recorded in transaction (f). (Credit
Cash, Debit Wages Payable - A & L)
Purchase of inventory on credit. (Debit Inventory, Credit Accounts Payable - A & L)
Payment of utility expenses. (Credit Cash, Debit Retained Earnings as Utility Expense -
A & SE)
Recorded depreciation on the equipment. (Credit Equipment, Debit Retained Earnings
as Depreciation Expense - A & SE)
�AP2-12B :
Calculate the following amounts for the month:
Sales revenue ($9000)
Cost of goods sold ($6000)
Total expenses other than cost of goods sold ($2200)
Net earnings or loss ($800)
Calculate the following amounts as at the end of the month:
1. Cash on hand ($9800) : 15000 (Cash from Investors ) - 4000 (Equipment Cost) -
500 (Supplies Cost) - 3000 (Debit Account Payable) + 4500 (Half of Inventory
Sold) - 300 (Dividends declared) - 1900 (Operating Expenses)
2. Total assets other than cash ($20700) : 15800 Equipment (4000-200+12000) +
400 Supplies (500-100) + 4500 (Accounts Receivable)
3. Total liabilities 3000 (Account Payable)
4. Share capital 27000 (Common Shares)
5. Retained earnings :
Net Income (800) - Dividends Declared (300) = 500
AP2-13B :
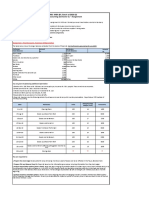
a. Prepare a statement of income for the year ended December 31, 2024.
- Refer to Excel Page
b. Calculate the amount of retained earnings as at December 31, 2024.
Retained Earnings : Opening Retained Earnings (410,000)
+ Net Income (368,000)
- Dividends Declared (180,000)
= Closing Retained Earnings of 598,000.
c. Prepare a classified statement of financial position as at December 31, 2024.
- Refer to Excel Page
UP2-3 :
● Sales and expenses in cash flow to see if the business is operating at a
sustainable rate at which they can pay the increased loan amount
○ Earnings before interest, taxes, depreciation, amortization (want to know
this to see if business is generating positive cash flow relative to the
amount of the loan)
● Other debts (to see how much there is that could disrupt the payment of the loan)
● Total Assets - both current & non-current (to see if there are sufficient collaterals,
in case the loan cannot be paid)