Halogens
The halogens are elements found in group VII of the periodic table, they includes:Fluorine ,
Chlorine, Bromine, Iodine and Astatine. These elements are highly reactive non-metals.
Occurrences of Halogens in Nature
1. Fluorine: It is often found in the form of fluorite (calcium fluoride) and cryolite (sodium
aluminum fluoride). Trace amounts of it also exists in minerals, water, and soil.
2. Chlorine: is commonly found as chloride ions in seawater, minerals such as halite (rock salt),
and in the form of various chlorides in soil.
3. Bromine: it exists mainly in seawater, from which it is extracted commercially. It is also found
in some minerals, such as silver bromide and beryllium bromide.
4. Iodine: occurs in seawater in small concentrations. It is also found in some minerals like silver
iodide and in trace amounts in certain plants and animals.
5. Astatine: it is a highly radioactive element with a very short half-life, so it is extremely rare
and exists only in trace amounts in nature. It is usually produced artificially in nuclear reactors.
ASSIGNMENT 3:
1. Using s,p,d,f notation, write the electronic configuration of all elements in group VII
2. With a balanced chemical equations, give three chemical properties of fluorine, chlorine,
bromine and iodine.
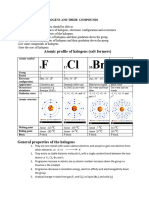
Physical Properties of Halogens (fluorine, chlorine, bromine, and iodine)
i. Their colour deepens down the group. Fluorine is yellow, Chlorine is greenish yellow,
Bromine is red and Iodine is violet.
ii. At room temperature, fluorine and chlorine are gases, bromine is liquid and iodine is solid.
iii. Their boiling point increases down the group due to increase in their atomic mass.
�iv. They are poor conduct of heat and electricity.
v. They have strong irritating smell.
Acidic Strengths of Halogens
The acid strengths of the halogens decreases down the group in the periodic table. This trend is
due to the increase in atomic size and decrease in electronegativity of the halogens.
HI > HBr > HCl > HF: decreasing order of their acidic strength.
The acid strength of hydrogen halides increases down the group due to increase in atomic size of
the halogen atom. This increase in size leads to a decrease in the strength of the hydrogen-
halogen bond, making it easier for the hydrogen ion (H⁺) to dissociate from the halide ion (X⁻).
Therefore, HF is the weakest acid, and HI is the strongest acid among HF, HCl, HBr and HI.
Oxycompounds of Halogens
Oxycompounds of halogens, particularly oxyacids of chlorine, are important chemical
compounds with various industrial and practical applications.
Preparation of Oxyacids of Chlorine
1. Chlorine water: oxyacids of chlorine can be prepared by dissolving chlorine gas in water to
form a mixture of hydrochloric acid (HCl) and hypochlorous acid (HOCl).
Cl2 + H2O HCl + HOCl
2. Direct synthesis: oxyacids of chlorine, such as hypochlorous acid (HOCl), chlorous acid
(HClO2), chloric acid (HClO3) and perchloric acid (HClO4) can also be prepared by direct
reaction of chlorine gas with water and appropriate reducing agents.
Properties of Oxyacids of Chlorine
They are strong oxidizing agents i.e they readily accept electrons from other substances
and making them to be oxidized.
� They are acidic in nature and their strength varies with perchloric acid being the strongest
and hypochlorous acid being the weakest.
They react with various substances such as metals, organic compounds, and reducing
agents to release of chlorine gas or other chlorinated compounds.
Applications
Oxyacids of chlorine have applications in various industries as:
Sterilization: due to strong antimicrobial properties of chlorine dioxide (ClO 2) derived
from HClO2; it is used in sterilizing of medical equipment, food processing equipment,
and in the pharmaceutical industry.
Disinfection: hypochlorous acid (HOCl) and chloric acid (HClO 3) are used for
disinfection in water treatment to kill bacteria, viruses, and other pathogens present in
water.
Bleaching agent: chlorine dioxide (ClO2) obtained from HClO2, is used in paper industry
to bleach wood pulp.
Disinfectant: hypochlorous acid (HOCl) is a powerful disinfectant and is commonly used
in household bleach, surface disinfection, and sanitizing solutions.
Chemical synthesis: perchloric acid (HClO4) is a strong oxidizing agent in chemical
synthesis.