0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes) 43 views12 pagesStacks and Queue by
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content,
claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online on Scribd
STACKS AND QUEUES
1] STACKS AND QUEUES:
Stack is a container of objects that are inserted and removed according to the Jast-in
first-out (LIFO) principle. Queue is a container of objects (a linear collection) that are inserted
and removed according to the first-in first-out (FIFO) principle.
stack and Queue both are the non-primitive data structures. The main differences
between stack and queue are that stack uses LIFO (last in first out) method to access and
add data elements whereas Queue uses FIFO (First in first out) method to access and add
data elements
Difference between Stack and Queue in Data Structures
= Key Stack Queue
No.
1 | Internal Stack is internally implemented | Onother hand Queue is implemented in such
Implementatio | in sucha way that the element ‘manner that the element inserted at the first
n inserted at the last in stack would | in queue would be the first element to come
be the first element tocome out | out of it So queue follows FIFO (First in and
of itSo stack follows LIFO (Last | First out).
in and First out)
Target clement | Incase of Stack operations on In case of Queue operations on element i.e
clement take place only from one | insertion takes place at the rear of the list and
end of the list called the top. the deletion takes place from the front of the
list.
3 | Labeland Flag | Instacks only one flag is While in case of queue two flags are
maintained to access the list maintained to access the list. The front flag
‘which always points to the last | always points to the first element inserted in
the list and is still present, and the rear flag
element present in the list.
always points to the last inserted element.
4 | Operation In Stack operations termed as While in case of Queue operations termed as
Push and Pop. Enqueue and dequeue.
5 | Implementatio | Stack does not have any variant] On other hand Queue has variants like
n and thus do not implemented circular queue, priority queue, doubly ended
further. queue.
6 | Complexity ‘As per above points the Stack is | On other hand Queue is more complex as
more simpler than Queue. compare to Stack.
TATAPUBLICATIONS�2.2 | STACKS
A Stack is a linear data structure that follows the LIFO (Last-In-First-Ouy) Pring,
“tack has one end, whereas the Queue has two ends (front and reat). It contains only ©
pointer top pointer pointing to the topmost element of the stack. Whenever an elemen,
sided in the stack, its added on the top of the stack, and the element can be delete!
rom the stack. In other words, a stack can be defined as a container in which insertion
Seletion can be done from the one end known as the top of the stack. x
Some key Points Related to Stack
1. Itis called as stack because it behaves like a real-world stack, piles of books, ot,
2 A Stack is an abstract data type with a pre-defined capacity, which means that ity
store the elements of a limited size.
3. It is a data structure that follows some order to insert and delete the elements,
that order can be LIFO or FILO.
any
Working of Stack
Stack works on the LIFO patter. As we can observe in the below figure there ay
five memory blocks in the stack; therefore, the size of the stack is 5.
Suppose we want to store the elements in a stack and let’s assume that stack is empiy
We have taken the stack of size 5 as shown below in which we are pushing the element
one by one until the stack becomes full.
~{] tel Hs
5-H
Since our stack is full as the size of the stack is 5, In the above cases, we can observe
‘hat it goes from the top to the bottom when we were entering the new element in the
stack. The stack gets filled up from the bottom to the top.
EQ
‘TATA PUBLICATIONS�>
DATA STRUCTURE
When we perform the delete operation on the stack, there is only one way for entry
and exit as the other end is closed. It follows the LIFO pattern, which means that the value
pone first will be removed last. In the above case, the value 5 is entered first, so it will
pe remov' ved only after the deletion of all the other elements.
F Applications of Stack
The following are the applications of the stack:
4, Balancing of Symbols: Stack is used for balancing a symbol. For example, we have
the following program:
int main()
: |
cout<<”Hello”;
cout<<“javaTpoint”; |
}
‘As we know, each program has an opening and closing braces; when the opening
braces come, we push the braces in a stack, and when the closing braces appear, we
pop the opening braces from the stack. Therefore, the net value comes out to be zero.
If any symbol is left in the stack, it means that some syntax occurs in a program.
2. String Reversal: Stack is also used for reversing a string. For example, we want to
reverse a “javaTpoint” string, so we can achieve this with the help of a stack.
First, we push all the characters of the string ina stack until w+ reach the null character.
After pushing all the characters, we start taking out the character one by one until we
teach the bottom of the stack.
3, UNDO/ REDO: It can also be used for performing UNDO/REDO operations. For
example, we have an editor in which we write ‘a’, then ‘b’, and then ‘c’; therefore
the text written in an editor is abc. So, there are three states, a, ab, and abc, which are
stored in a stack. There would be two stacks in which one stack shows UNDO state,
and the other shows REDO state.
If we want to perform UNDO operation, and want to achieve ‘ab’ state, then we
implement pop operation. a
‘TATAPUBLICATIONS�ion is calling itself again. 7,
Recursion: The recursion means that ica ne stack in which all ae aintay
the previous states, the compiler creates 4 SY° " © Previoy,
records of the function are maintained.
‘4 na Graph, an
5. DFS(Depth First Search): This search is implemented o ix 'd Graph Us
the stack data structure
maze prob]
6. Backtracking: Suppose we have to create a path to ae the tn vit .
moving in a particular path, and we realize that we
e pl at the new positi
Le. top=top+1, and the element will be placed at the Position of th, top ey
of
The elements will be inserted until we reach the max size of the stack
tops
Stack hal
POP Operation
The steps involved in the POP operation is given below:
Before deleting the element from the stack, we check whether the stack is empty.
If we try to delete the element from the empty stack, then the underflow Condition,
occurs.
If the stack is not empty, we first access the element which is pointed by the top
Once the pop operation is performed, the top is decremented by 1, ie., top=top-1.
top=2 top=4
+~pop=40 4wsS tara Puruicarionss
—_�a
DATASTRUCTURE
eee
Types Of Queues
There are four types of Queues:
Linear Queue: In Linear Queue, an insertion takes place from one end while the
deletion occurs from another end, The end at which the insertion takes place is known
as the rear end, and the end at which the deletion takes place is known as front end.
t strictly follows the FIFO rule. The linear Queue can be represented, as shown in
the below figure:
Bn
front rear
The above figure shows that the elements are inserted from the rear end, and if we
insert more elements in a Queue, then the rear value gets incremented on every
insertion. If we want to show the deletion, then it can be represented as:
Ra le
front rear
In the above figure, we can observe that the front pointer points to the next element,
and the element which was previously pointed by the front pointer was deleted.
‘The major drawback of using a linear Queue is that insertion is done only from the
rear end. If the first three elements are deleted from the Queue, we cannot insert
more elements even though the space is available in a Linear Queue. In this case, the
linear Queue shows the overflow condition as the rear is pointing to the last element
of the Queue.
2 Circular Queue: In Circular Queue, all the nodes are represented as circular. It is
similar to the linear Queue except that the last element of the queue is connected to.
the first element. It is also known as Ring Buffer as all the ends are connected to
Ga
another end. The circular queue can be represented as:
TATA PUBLICATIONS�linear queue is overcome by using the circular queye
The drawback that occurs in a . ;
e new element can be 7
added in
available in a circular queue,
If the empty space is
i the value of rear.
an empty space by simply incrementin}
Priority Queue: A priority queue is another special type of Queue data structure in
which each element has some priority associated with it. Based on the priority of the
arranged ina priority queue. If the elements occur with the
cording to the FIFO principle.In priority Queue
arrival while the deletion occurs based on the
element, the elements are
same priority, then they are served a
the insertion takes place based on the
priority. The priority Queue can be shown as:
The above figure shows that the highest priority element comes first and the elements
of the same priority are arranged based on FIFO structure.
Deque: Both the Linear Queue and Deque are different as the linear queue follows
the FIFO principle whereas, deque does not follow the FIFO principle. In Deque, the
insertion and deletion can occur from both ends.�DATA STRUCTURE
seacks: A Stack is a linear data structure that follows the LIFO (Last-In-First-Out)
principle. Stack has one end, whereas the Queue has two ends (front and rear). It
contains only one pointer top pointer pointing to the topmost element of the stack
Whenever an element is added in the stack, it is added on the top of the stack, and
the element can be deleted only from the stack. In other words, a stack can be defined
as a container in which insertion and deletion can be done from the one end known
as the top of the stack.
q working of Stack: Stack works on the LIFO pattern. As we can observe in the
pelow figure there are five memory blocks in the stack; therefore, the size of the
stack is 5.
Suppose we want to store the elements in a stack and let’s assume that stack is empty.
We have taken the stack of size 5 as shown below in which we are pushing the
elements one by one until the stack becomes full.
POP Operation: The steps involved in the POP operation is given below:
1. Before deleting the element from the stack, we check whether the stack is empty.
2, Ifwetry to delete the element from the empty stack, then the underflow condition
occurs.
3, If the stack is not empty, we first access the element which is pointed by the top
4. Once the pop operation is performed, the top is decremented by 1, ice.,
top=top-1.
4, Queues: A queue in the data structure can be considered similar to the queue in the
realworld. A queue is a data structure in which whatever comes first will go out first.
It follows the FIFO (First-In-First-Out) policy. In Queue, the insertion is done from
one end known as the rear end or the tail of the queue, whereas the deletion is done
from another end known as the front end or the head of the queue. In other words,
it can be defined as a list or a collection with a constraint that the insertion can be
performed at one end called as the rear end or tail of the queue and deletion is
performed on another end called as the front end or the head of the queue.
Linear Queue: In Linear Queue, an insertion takes place from one end while the
deletion occurs from another end. The end at which the insertion takes place is known
as the rear end, and the end at which the deletion takes place is known as front end.
It strictly follows the FIFO rule.
NTAPUBLICATIONS�all the nodes are represented as circ) It
last element of the queue is connecteq *
all the ends are connectey
t
Circular Queue: In Circular Queue,
similar to the linear Queue except that the |
the fret element. It is aloo kncifenies aan ES
another end.
Priority Queue: A priority queue is another special type of Queue data structure i,
which wach slerent has gonna poor, 2s°oaniaene © Based on the priority of y,
veruect the deents are ariangedina peSuMCEES the elements occur with t,
same priority, then they are served according to the FIFO principle.In priority Quey,
the insertion takes place based on the arrival while the deletion occurs based on th,
priority.
a ee
a
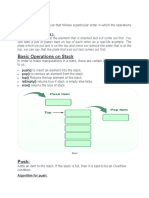
What is a Stack? What are the operations that can be performed on a stack?
Discuss the algorithms for push and pop operations on a stack.
What is stack? Discuss about array and linked representation of a stack.
What is a Queue? Explain its operations.
What is a queue? Explain types of queue.
a