Do not write
10 outside the
box
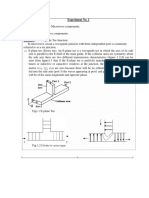
0 4 Figure 4 shows an arrangement used to investigate double slit interference using
microwaves. Figure 5 shows the view from above.
Figure 4
Figure 5
The microwaves from the transmitter are polarised. These waves are detected by
the aerial in the microwave receiver (probe). The aerial is a vertical metal rod.
The receiver is moved along the dotted line AE. As it is moved, maximum and
minimum signals are detected. Maximum signals are first detected at points B and
C. The next maximum signal is detected at the position D shown in Figure 5.
Figure 5 shows the distances between each of the two slits, S1 and S2, and the
microwave receiver when the aerial is in position D.
S1D is 0.723 m and S2D is 0.667 m.
*10*
IB/M/Jun17/7407/1
� Do not write
11 outside the
box
0 4 . 1 Explain why the signal strength falls to a minimum between B and C, and between
C and D.
[3 marks]
0 4 . 2 Determine the frequency of the microwaves that are transmitted.
[3 marks]
frequency = Hz
Question 4 continues on the next page
Turn over ►
*11*
IB/M/Jun17/7407/1
� Do not write
12 outside the
box
0 4 . 3 The intensity of the waves passing through each slit is the same.
Explain why the minimum intensity between C and D is not zero.
[2 marks]
0 4 . 4 The vertical aerial is placed at position B and is rotated slowly through 90° until it
lies along the direction AE.
State and explain the effect on the signal strength as it is rotated.
[3 marks]
11
*12*
IB/M/Jun17/7407/1