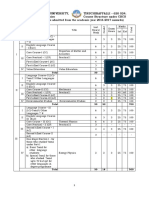
Group A: Semester I
Sr. Subject Evaluation Scheme (Marks)
Category Subject L T P/D Credits
No. Code IA ESE Subject Total
Theory:
1 FC PHY-111 Applied Physics 3 1 0 4 40 60 100
2 FC HS-111 Communication Skills 3 0 0 3 40 60 100
Basic Electrical
3 FC EE-111 3 1 0 4 40 60 100
Engineering
4 FC MA-111 Applied Mathematics-1 3 1 0 4 40 60 100
5 MC EVS-111 Energy and Environment 2 1 0 3 40 60 100
Labs: IA ESVE Sub. Total
1 FC PHY-111P Applied Physics Lab 0 0 2 1 30 20 50
2 FC HS-111P Communication Skills Lab 0 0 2 1 30 20 50
3 FC EE-111P Basic Electrical 0 0 2 1 30 20 50
Engineering Lab
4 FC *WXX- Workshop 0 0 4 2 30 20 50
111P
Total 14 04 10 23 700
Group A: Semester II
Sr. Subject Evaluation Scheme (Marks)
No. Category Code
Subject L T P/D Credits IA ESE Subject Total
Theory:
1 FC CHM-111 Applied Chemistry 3 1 0 4 40 60 100
2 FC CS-111 Computer Programming 3 0 0 3 40 60 100
Basic Electronics
3 FC EC-111 3 1 0 4 40 60 100
Engineering
4 FC MA-121 Applied Mathematics-II 3 1 0 4 40 60 100
Universal Human Values
5 MC UHV-111 and Awareness About 3 0 0 3 40 60 100
Himachal Pradesh
Labs: IA ESVE Sub. Total
1 FC CHM-111P Applied Chemistry Lab 0 0 2 1 30 20 50
Computer Programming
2 FC CS-111P 0 0 2 1 30 20 50
Lab
Basic Electronics
3 FC EC-111P 0 0 2 1 30 20 50
Engineering Lab
4 FC ME-111P Engineering Graphics 0 0 4 2 30 20 50
and Design
5 MC HS-122P Holistic Health and Yoga 0 0 2 1 30 20 50
Total 15 03 12 24 750
Legends: L- Lecture ESE - End Semester Examination
T - Tutorial FW - Documentation/ File work and presentation
P - Practical LP - Lab performance
CT - Class Test ESVE - End Semester Exam. / Viva-voce Exam.
IA - Internal Assessment MC-Mandatory Course
FC- Foundation Course
*WXX where XX is branch code- CE (Civil Engineering), CS (Computer Science & Engineering), IT
(Information & Technology), EC (Elect. Comm. & Engineering)
3
� PHY-111 Applied Physics
Teaching
Marks Distribution
Scheme Duration of End
Credit
End Semester
L T P Internal Assessment Total
Semester Examination
Maximum Marks: 40 Maximum Marks: 60 100
3 1 0 4 3 Hours
Minimum Marks: 16 Minimum Marks: 24 40
Guidelines for setting Question Paper: Question paper of end semester examination will be of 60
marks. The question paper will consist of five sections A, B, C, D and E. Sections A, B, C and D will
have 2 questions of 12 marks each and section E has short answer type questions consisting of six parts
of 02 marks each. The candidates will attempt five questions in all, i.e. one question each from sections
A, B, C, D and the compulsory question from section E. In the question paper, the questions available
in sections A, B, C and D will be covered from Unit-I, Unit-II, Unit-III and Unit-IV respectively and
Section-E will cover the whole syllabus.
Course Contents:
Unit-I:
Theory of Relativity: Inertial and non- inertial frames of reference, earth as an inertial frame of reference, Michelson
and Morley experiment, Postulates of special theory of relativity, Galilean and Lorentz transformations, Time
dilation and length contraction, Relativistic kinematics and mass-energy equivalence.
Laser: Introduction, Characteristics of lasers, Spontaneous and stimulated emission of radiation Einstein's
coefficients, Population inversion, Ruby laser, Helium -Neon lasers & Semiconductor Lasers Applications of laser
in industry, Scientific and medical fields.
Unit–II:
Oscillations: Simple harmonic motion (SHM), Differential equation of SHM, Energy of SHM, Damped andForced
Oscillations, Relaxation Time, Quality Factor, Resonance, Sharpness of Resonance.
Fiber Optics: Fundamental ideas about optical fiber, Propagation mechanism, Acceptance angle and acceptance
cone, Numerical aperture, Propagation Mechanism and communication in fiber, Single and Multi-Mode Fibers, Step
index and Graded index fiber, Attenuation and losses, Applications of optical fibers.
Unit–III
Quantum Mechanics: De Broglie waves, Phase and Group velocity concept, Uncertainty principle and its
applications, Wave function, Postulates of quantum mechanics, Derivation of Schrodinger equation for time
independent and time dependent cases and its applications viz. Particle in one dimensional box.
X-rays: X-rays production, hard and soft x-rays, Continuous and characteristics x-rays, Bremsstrahlung effect
Unit-IV:
Electrodynamics: Equation of continuity, displacement current, Maxwell‘s equations, wave equation for
electromagnetic radiation, electromagnetic wave propagation in free space and isotropic dielectric medium, Poynting
vector & Poynting theorem.
Superconductivity: Introduction and discovery of superconductivity, Meissner effect, Type-I and type-IIP
superconductors, Isotope effect, BCS theory (qualitative), High temperature superconductors, Applications of
superconductivity.
Textbooks:
• Engineering Physics, H.K Malik & A.K Singh, Tata McGraw-Hill.
• Ajoy Ghatak, Quantum Mechanics: Theory and Applications‖, Tata McGraw-Hill.
• Satya Prakash and Vibhav saluja, Engineering Physics‖, Pragti Prakashan Meerut.
• Applied Solid State Physics‖, Wiley India Pvt Ltd.
Reference Books:
• Ajoy Ghatak, ―Optics‖, Tata McGraw-Hill.
• N. Subrahmanyam, Brij Lal, M.N. Avadhanulu, ―Optics‖, S. Chand & Co. Ltd.
• Anuradha De, ―Fiber optics and laser Principles and Applications‖, New Age International.
• Arthur Beiser, ―Concepts of Modern Physics‖, Tata McGraw-Hill.
• David J Griffiths, ―Introduction to electrodynamics‖, Prentice Hall of India, New Delhi
8
� HS-111 Communication Skills
Teaching
Marks Distribution
Scheme Duration of End
Credit
End Semester
L T P Internal Assessment Total
Semester Examination
Maximum Marks: 40 Maximum Marks: 60 100
3 0 0 3 3 Hours
Minimum Marks: 16 Minimum Marks: 24 40
Guidelines for setting Question Paper: Question paper of end semester examination will be of 60 marks.
The question paper will consist of five sections A, B, C, D and E. Sections A, B, C and D will have 2
questions of 12 marks each and section E has short answer type questions consisting of six parts of 02 marks
each. The candidates will attempt five questions in all, i.e. one question each from sections A, B, C, D and
the compulsory question from section E. In the question paper, the questions available in sections A, B, C
and D will be covered from Unit-I, Unit-II, Unit-III and Unit-IV respectively and Section-E will cover the
whole syllabus.
Course Contents:
Unit-I:
Essentials of communication: The meaning, types &process of communication, Barriers to communication and
removal of these barriers, Shannon & weaver model of communication, Berlos‘ model of communication, The
Seven Cs of Effective Communication - Completeness, Conciseness, Consideration, Concreteness, Clarity,
Courtesy, Correctness, Types of information- order, advise, suggestion, motivation, persuasion, warning and
education. Mass Communication –function of mass communication – Media of mass communication, Advantages
and disadvantages of social media.
Unit–II:
Essentials of Grammar: Types of sentences: Declarative Sentence, Imperative Sentence, Interrogative Sentence,
Exclamatory Sentence, simple, compound & complex sentences, conversion of one type of sentence into other,
Parts of speech, Tenses, articles and prepositions, Model Auxiliaries Types of diction, ways to improve diction,
Paragraph writing.
Unit–III
Technical Communication: Report writing: Characteristics of a good report, parts & types of reports, drafting of
reports. Business letters: planning a business letter, parts of a letter, classification of business letters – inviting and
sending quotations, letter placing orders, letter of complaint, letter of adjustment, and letter of Job, letter negotiating
a job offer and Resume writing, Drafting memorandum, notices, agenda and minutes of meeting, preparing
effective e- mail messages and power-point presentations
Unit-IV:
Soft skills & personality development: Soft skills: Classification of soft skills, Delivering effective
presentations,Capturing audience, Impromptu speech, speech initiators, telephone etiquette - Good practice
when making and receiving a call; Becoming a good leader and team-player, Personal SWOT analysis.,
body language, Types ofinterviews, preparing for a job interview, Strategies for managing emotions & controlling
Stress.
Textbooks:
• Communication Skills, Sanjay Kumar and Pushp Lata, Oxford University Press.
• Effective Communication and soft Skills, Nitin Bhatnagar and Mamta Bhatnagar, Pearson Publication.
• Communicative English for Engineers and professionals, Nitin Bhatnagar and Mamta Bhatnagar,
Pearson Publication.
• Personality and Soft Skills by B. K. Mitra Oxford press.
• An Introduction to Professional English and Soft Skills: by Bikram K. Das, Kalyani Samantray,
Cambridge Press.
• Business correspondence and Report Writing: by R. C. Sharma & Krishna Mohan
Reference Books:
• Business Communication: Theory and Application by R.W. Lesikar and John.D. Pettit , All India
Traveller Bookseller.
• Speaking and Writing for Effective Business Communication by Francis Soundaraj Macmillan.
• Understanding Human Communication by Ronald B. Adler and George Rodman Oxford University
9
� EE-111 Basic Electrical Engineering
Teaching
Marks Distribution
Scheme Duration of End
Credit
End Semester Semester Examination
L T P Internal Assessment Total
Examination
Maximum Marks: 40 Maximum Marks: 60 100
3 1 0 4 3 Hours
Minimum Marks: 16 Minimum Marks: 24 40
Guidelines for setting Question Paper: Question paper of end semester examination will be of 60 marks. The
question paper will consist of five sections A, B, C, D and E. Sections A, B, C and D will have 2 questions of 12
marks each and section E has short answer type questions consisting of six parts of 02 marks each. The candidates
will attempt five questions in all, i.e. one question each from sections A, B, C, D and the compulsory question from
section E. In the question paper, the questions available in sections A, B, C and D will be covered from Unit-I,
Unit-II, Unit-III and Unit-IV respectively and Section-E will cover the whole syllabus.
Course Contents:
Unit-I:
DC Circuits: Kirchhoff‘s voltage and current laws; power dissipation; Voltage source and current source; Mesh and
Nodal analysis; Star-delta transformation; Superposition theorem. Thevenin‘s theorem; Norton‘s theorem; Maximum
power transfer theorem; Millman‘s theorem and Reciprocity theorem; Transient response of series RL and RC circuits.
Unit–II:
Steady state analysis of DC Circuits: The ideal capacitor, permittivity; the multi- plate capacitor, variable
capacitor; capacitor charging and discharging, current-voltage relationship, time-constant, rise-time, fall-
time,inductor energization and de- energization, inductance current-voltage relationship, time-constant; Transient
response of RL, RC and RLC Circuits.
Unit–III
AC Circuits: Sinusoidal sources, RC, RL and RLC circuits, Concept of Phasors, Phasor representation of circuit
elements, Complex notation representation, Single phase AC Series and parallel circuits, power dissipation in AC
circuits, power factor correction, Resonance in series and parallel circuits, Balanced and unbalanced 3-phase circuit -
voltage, current and power relations, 3-phase power measurement, Comparison of single phase and three phase supply
systems. Electromagnetism: Electromagnetic induction, Dot convention, Equivalent inductance, Analysis of Magnetic
circuits, AC excitation of magnetic circuit, Iron Losses, Fringing and stacking, applications: solenoids and relays.
Unit-IV:
Single Phase Transformers: Constructional features of transformer, operating principle and applications, equivalent
circuit, phasor analysis and calculation of performance indices. Motors and Generators: DC motor operating
principle, construction, energy transfer, speed torque relationship, conversion efficiency, applications, DC generator
operating principle, reversal of energy transfer, EMF and speedrelationship, applications.
Textbooks:
• Ashfaq Husain and Harroon Ashfaq Fundamental of Electrical Engineering Dhanpat Rai & Co. (P) Limited;
Fourth edition, 1 January 2016
• Nagrath I.J. and D. P. Kothari (2001), Basic Electrical Engineering, Tata McGraw Hill.
• Hayt and Kimberly, Engineering Circuit Analysis, Tata McGraw Hill.
• Ritu Sahdev (2019), Basic Electrical Engineering, Khanna Book Publishing Company
• Kulshreshtha D.C. (2009), Basic Electrical Engineering, Tata McGraw Hill.
• Rajendra Prasad (2009), Fundamentals of Electrical Engineering, Prentice Hall, India
Reference Books:
• Ajoy Ghatak, ―Optics‖, Tata McGraw-Hill.
• N. Subrahmanyam, Brij Lal, M.N. Avadhanulu, ―Optics‖, S. Chand & Co. Ltd.
• Anuradha De, ―Fiber optics and laser Principles and Applications‖, New Age International.
• Arthur Beiser, ―Concepts of Modern Physics‖, Tata McGraw-Hill.
• David J Griffiths, ―Introduction to electrodynamics‖, Prentice Hall of India, New Delhi
11
� MA-111 Applied Mathematics-I
Teaching
Scheme Marks
Credit Duration of End
Distribution
End Semester
L T P Internal Semester Tota Examination
Assessment Examinatio l
n
Maximum Marks: Maximum Marks: 100
3 1 0 4 40 60 3
Minimum Marks: Minimum Marks: 40 Hours
16 24
Guidelines for setting Question Paper: Question paper of end semester examination will be of 60 marks. The
question paper will consist of five sections A, B, C, D and E. Sections A, B, C and D will have 2 questions of 12
marks each (Each subdivided into at least two equal sub-parts) and section E has short answer type questions
consisting of six parts of 02 marks each or twelve parts of 01 marks each. The candidate will attempt five questions
in all, i.e one question each from sections A, B, C, D and the section E will be compulsory. In the question paper,
the questions available in sections A, B, C and D will be covered from Unit-I, Unit-II, Unit-III and Unit-IV
respectively and section-E will cover whole syllabus
Course Contents:
Unit-I:
Linear Algebra: Review of matrices, Row reduced echelon form, Inverse using Gauss Jordan method and rank
of a matrix, Solution of linear system of equations; Gaussian elimination, LU decomposition method. Vector
space, subspaces, Linear dependence & Independence of vectors, basis and dimension, rank-nullity theorem,
Eigen values, Eigen vectors, diagonalization. Cayley Hamilton Theorem (without proof), quadratic & canonical
forms.
Unit–II:
Calculus: Rolle’s theorem, Lagrange’s mean value theorem (without proof), improper integrals, beta and
gamma functions. Functions of several variables, Limits and continuity, partial derivatives, total derivative,
Euler ‘s theorem, Jacobian, maxima and minima, Lagrange ‘s method of multipliers, Taylor ‘s & Maclaurin
‘s Theorem.
Unit–III
Multiple Integrals: Double integral, change of order of integration, Polar coordinates, graphing of polar
curves, Change of variables, Applications of double integrals to areas and volumes, evaluation of triple
integral.
Unit-IV:
Functions of Complex variables: Introduction to elementary complex functions (exponential, trigonometric
& hyperbolic, inverse trigonometric & hyperbolic, logarithmic), Analytic functions, Cauchy-Riemann
equations.
Complex integration: Cauchy’s theorem, Cauchy’s integral formula, Taylor’s & Laurent’s series, zeros &
singularities, Cauchy’s residue theorem.
Textbooks:
• B. S. Grewal, Higher Engineering Mathematics by B. S. Grewal 43rd Edition (2015)
• Thomas, G.B. and Finney, R.L., Calculus and Analytic Geometry, Pearson Education (2007),9thed.
• Stewart James, Essential Calculus; Thomson Publishers (2007), 6th ed.
• R.K. Jain and S.R.K. Iyengar, Advanced Engineering Mathematics (2003), 2nd ed.
Reference Books:
• Wider David V, Advanced Calculus: Early Transcendentals, Cengage Learning (2007).
• Apostol Tom M, Calculus, Vol I and II, John Wiley (2003).
• H.K. Dass and Rajnish Verma, ―Engineering Mathematic, S. Chand Publications.
• Erwin Kreyszig, Advanced Engineering Mathematics, John Wiley & Sons (2011) 9th Edition.
12
� EVS-111 Energy and Environment
Teaching
Marks Distribution
Scheme Duration of End
Credit
End Semester Semester Examination
L T P Internal Assessment Total
Examination
Maximum Marks: 40 Maximum Marks: 60 100
2 1 0 3 3 Hours
Minimum Marks: 16 Minimum Marks: 24 40
Guidelines for setting Question Paper: Question paper of end semester examination will be of 60 marks. The
question paper will consist of five sections A, B, C, D and E. Sections A, B, C and D will have 2 questions of 12
marks each and section E has short answer type questions consisting of six parts of 02 marks each. The candidates
will attempt five questions in all, i.e. one question each from sections A, B, C, D and the compulsory question from
section E. In the question paper, the questions available in sections A, B, C and D will be covered from Unit-I,
Unit-II, Unit-III and Unit-IV respectively and Section-E will cover the whole syllabus.
Course Contents:
Unit-I:
Ecosystems: Structure and function of an ecosystem–ecological succession–primary and secondary succession -
ecological pyramids – pyramid of number, pyramid of energy and pyramid of biomass. Conventions on Climate
Change: Origin of Conference of Parties (COPs), United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change
(UNFCCC) and Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC); Kyoto Protocol, Montreal Action Plan; Paris
Agreement and post-Paris scenario. Environmental issues: Global Environmental crisis, Current global environment
issues, Global Warming, GreenhouseEffect, role of Carbon Dioxide and Methane, Ozone Problem, CFC‗s and
Alternatives, Causes of Climate change,
Carbon footprint.
Unit–II:
Air Pollution: Origin, sources, adverse effects and preventive measures related to air pollution. Case study for air
pollution (London smog, Photochemical smog, Bhopal gas tragedy). Water Pollution: Origin, sources, adverse effects
and preventive measures related to water pollution. Case study for air pollution (Minamata tragedy, Arsenic pollution at
Punjab/UP, The Ganga River pollution). Noise Pollution: Origin, sources, adverse effects and preventive measures related
to noise pollution. Nuclear pollution: Origin, sources, adverse effects and preventive measures related to radioactive
pollution, Case study. Environmental protection acts: Important environmental protection acts in India – water, air
(prevention and controlof pollution) act, wild life conservation and forest act.
Unit–III
Renewable and non-renewable resources: Coal, Petroleum, Solar energy, wind energy, hydrothermal energy, nuclear
energy, Tidal energy, Bioenergy etc. Role of individual in conservation of natural resources for sustainable life styles.
Use and over exploitation of Forest resources, Deforestation, Timber extraction, Mining, Dams and their effects on
forest and tribal people. Use and over exploitation of surface and ground water resources, Floods, Drought, Conflicts
over water, Dams- benefits and problems. National green hydrogen mission. FAME India Scheme.
Unit-IV:
Environment and Disaster: Introduction: Principles of Disaster Management. Natural Disasters such as Earthquake,
Floods, Fire, Landslides, Tornado, Cyclones, Tsunamis, Nuclear and Chemical Terrorism. Hazards, Risks and
Vulnerabilities, Vulnerability of a location and vulnerable groups, National policy on disaster Management.
Textbooks:
• Moaveni, S., Energy, Environment and Sustainability, Cengage(2018)
• Down to Earth, Environment Reader for Universities, CSE Publication(2018)
• Chapman, J.L. and Reiss, M.J., Ecology Principles and Application, Cambridge University Press (LPE)
(1999).
• Eastop, T.P. and Croft, D.R., Energy Efficiency for Engineers and Technologists, Longman and Harow (2006).
• O‘Callagan, P.W., Energy Management, Mc Graw Hill Book Co. Ltd.(1993).
• Peavy H.S. and Rowe D.R. Environmental Engineering, McGraw Hill(2013)
13